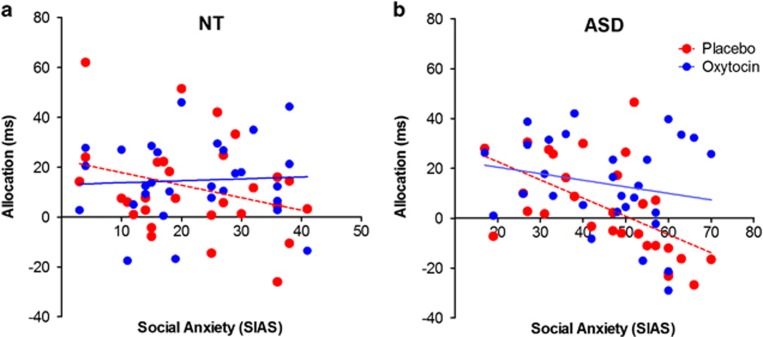
Figure 3.
Association between the allocation of attention to faces in the dot-probe task and social anxiety in both groups and its modulation by oxytocin administration. (a) In the neurotypical control group, social anxiety showed a weak negative association with attention to faces under placebo (r=−0.30, P=0.119), which vanished following oxytocin administration (r =0.05, P=0.785). (b) In the autistic group, social anxiety significantly predicted attentional avoidance of faces under placebo (r=−0.56, P<0.05), whereas this association was no longer significant under oxytocin (r=−0.20, P=0.289). ASD, autism spectrum disorder; NT, neurotypical; SIAS, Social Interaction Anxiety Scale.