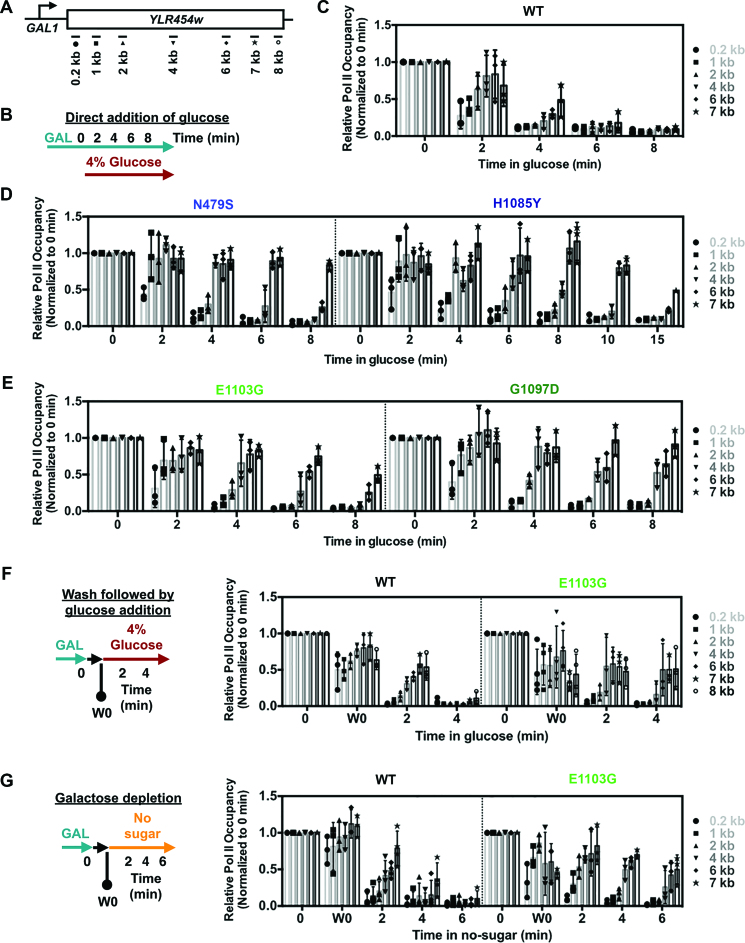
Figure 5.
Pol II catalytic mutants show slower in vivo elongation rate in a glucose shutoff ChIP assay. (A) Schematic of the GAL1p::YLR454w with positions of PCR amplicons used for ChIP experiments. (B) Schematic of the regular glucose shutoff experiment used in (C) and (D). In vivo apparent elongation rate for WT (C), LOF (D; N479S and H1085Y) and GOF (E; E1103G and G1097D) catalytic mutants determined by ChIP upon glucose shutoff of transcription by direct addition of glucose (to 4% final concentration) to the mid-log grown culture in YPGal at 30°C. Values were normalized to pre-glucose addition (0 min) and error bars represent standard deviation of the mean for at least three independent experiments. For H1085Y, longer time point (10 and 15 min) values obtained from two repeats, with error bars indicating the range of the two experiments. (F) Glucose shutoff assay to compare apparent in vivo elongation rate between WT and fast catalytic mutant (E1103G) following the Hazelbaker et al. protocol (19). Pre-glucose addition sample (0 min) was isolated as described in Figure 5A; subsequently cells were washed in synthetic complete medium lacking carbon source and inoculated in YPD (4% glucose) to shutoff the transcription. One wash 0 (W0 min) sample was isolated after the washing and before shutoff to determine the effect of washing. Values were normalized to pre-glucose addition (0 min) and error bars represent standard deviation of the mean of at least three independent repeats. (G) Galactose depletion to determine apparent elongation rate in WT and fast catalytic mutant (E1103G). Pre-glucose (0 min) and wash 0 (W0 min) samples were taken as described in Figure 5F, followed by inoculation of cells into synthetic medium lacking any sugar to incur transcriptional shutoff due to galactose depletion. Values were normalized to pre-glucose addition (0 min) and error bars represent standard deviation of the mean for at least three independent repeats.