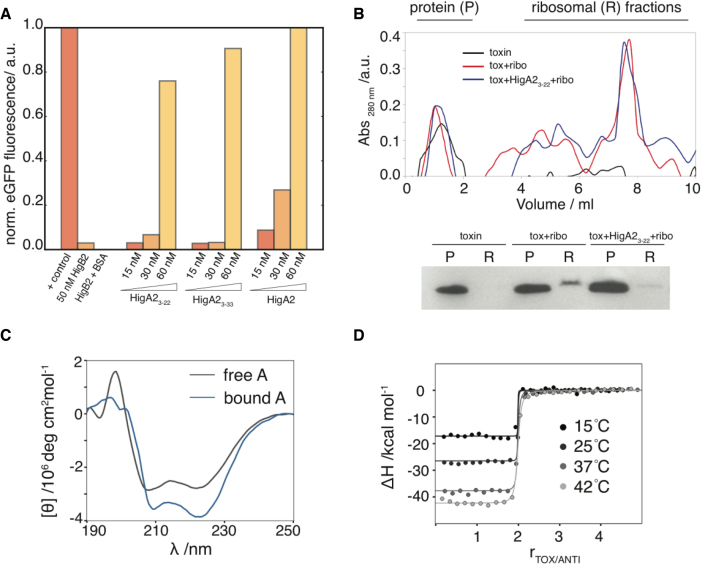
Figure 3.
Inhibition of the VcHigB2 toxin by the VcHigA2 antitoxin. (A) Fluorescent reporter protein is synthesized in the in vitro translation assay and addition of VcHigB2 toxin (at 50 nM, 10 times above its IC50) inhibits its synthesis. Addition of BSA (at 1 μM) has no effect on toxin activity, while peptides derived from the N-terminus of VcHigA2 antitoxin (VcHigA23-22 and VcHigA23-33) as well as full-length antitoxin inhibit toxin activity. Concentration of VcHigB2 toxin was constant 50 nM. Fluorescence of the reporter protein (eGFP) was normalized using the values for the positive (no toxin) and negative controls (no eGFP coding fragment). (B) Top: ribosome profiles from ultracentrifugation on a sucrose gradient. Bottom: anti-his western blot of the protein and ribosomal fractions show that VcHigA23-22 prevents binding of the VcHigB2 toxin to the ribosome. (C) Binding to the toxin is coupled by the folding of the antitoxin. CD spectrum of the bound antitoxin estimated as the difference spectrum between VcHigBA2 complex and VcHigB2. (D) Calorimetric titrations of toxin into antitoxin performed at different temperatures. Global fits of the model function (Equation 1) to the data measured at different temperatures are shown as solid lines.