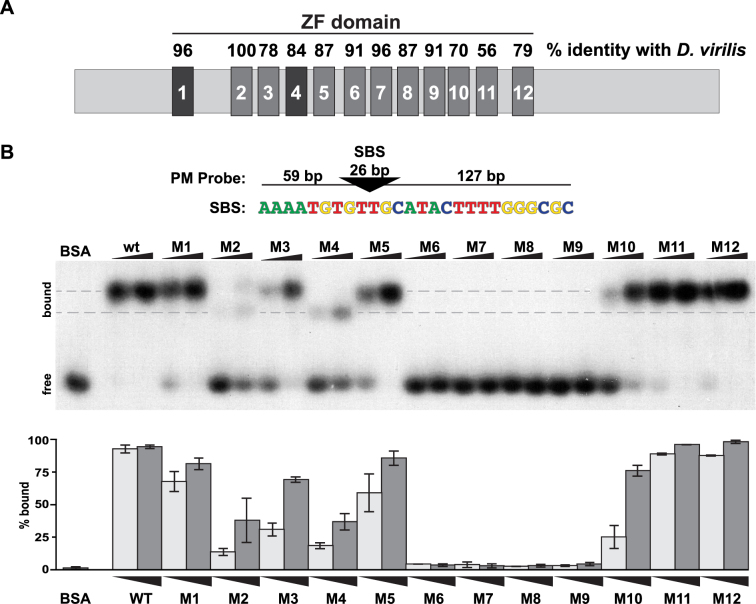
Figure 3.
Analyses of in vitro binding properties of Su(Hw) ZF mutants. (A) Shown is a diagram of the ∼110 kD Su(Hw) protein with each ZF represented as a large rectangle. The ZFs are tightly clustered, with amino acid spacing ranging from 47 amino acids between ZF1 and ZF2 to 3 amino acids between ZF8 and ZF9. The domain includes two C2HC ZFs (ZF1, ZF4) and 10 C2H2 ZFs. The percent of amino acid identity between the Drosophila melanogaster Su(Hw) ZFs and the corresponding Drosophila virilis ZFs is indicated above each rectangle. (B) Top: the structure of the 212-bp DNA probe (PM) is shown, with the 26-bp SBS (triangle) located 59 bp from the 5΄ and 127 bp from the 3΄ end. The nucleotide sequence of the Su(Hw) binding consensus is indicated below the triangle. Bottom: shown is a representative image of an EMSA, comparing DNA binding of Su(Hw)WT and Su(Hw)M proteins that carry a replacement of zinc-chelating amino acids in the indicated ZF, referred to as Mutant (M)1 to M12. Bovine serum albumin (1.0 μg) serves as a negative control. Binding was assayed using two protein amounts (0.3 and 1.0 μg). The migration of free and bound DNA is indicated on the left. Gray dashes indicate the locations of two Su(Hw)–DNA complexes with different migrations. Quantification of the percent of bound probe for each Su(Hw) protein is graphed (0.3 μg, light gray; 1.0 μg, dark gray). Quantification represents an average of two replicates, with the bars showing the range of values obtained.