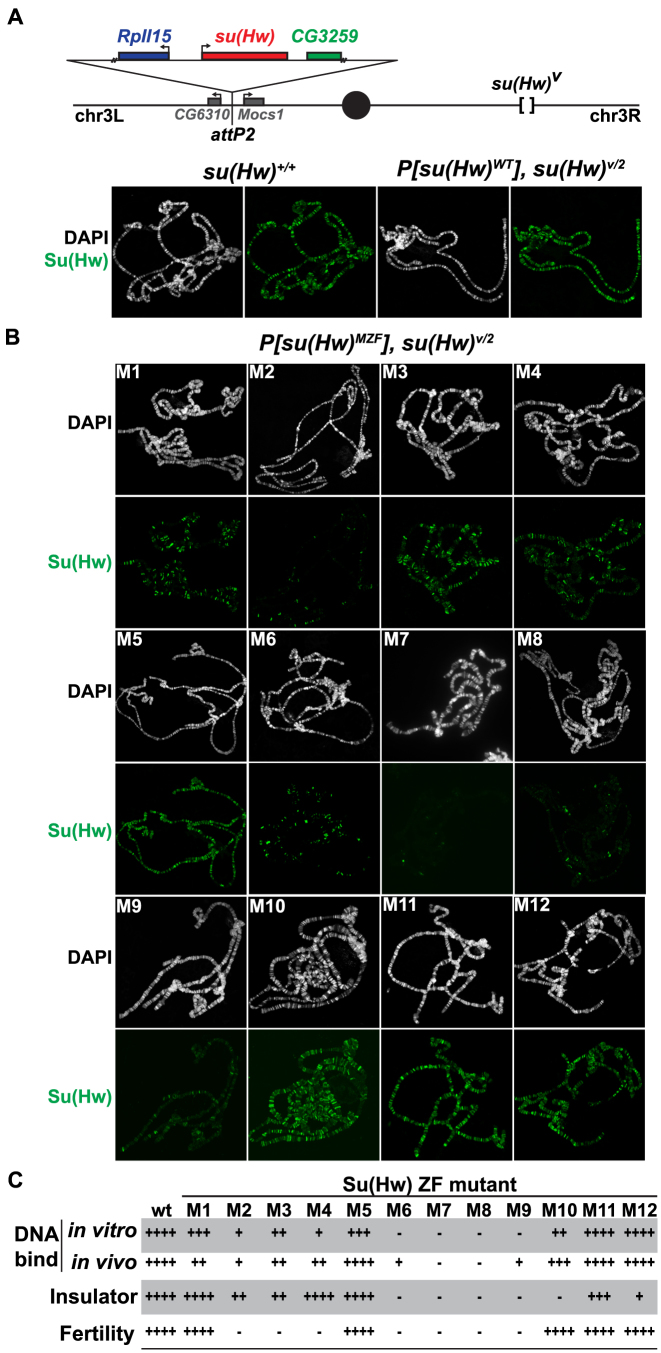
Figure 4.
Analyses of in vivo function of Su(Hw) ZF mutants. (A) Top: schematic of the third chromosome organization in su(Hw) transgenic flies. Transgenes were inserted into the attp2 landing site located between the CG6310 and Mocs1 genes. Each transgene carried a 6-kb genomic fragment, which included 1.2 kb of 5΄ DNA encompassing the complete RpII15 gene (blue rectangle), a wild-type or mutant su(Hw) gene (red rectangle) and 0.5 kb of 3΄ DNA that encompassed a portion of CG3258 (green rectangle). Transgenes were recombined onto a su(Hw)v chromosome. Bottom: shown is the salivary gland polytene chromosome distribution of endogenous Su(Hw) [su(Hw)+/+] and wild-type Su(Hw) expressed from the transgene [P[su(Hw)WT, su(Hw)v/2]. Chromosomes were stained with the DAPI (white) and antibodies against Su(Hw) (green). (B) Shown is the polytene chromosome distribution of the Su(Hw) mutant proteins. Mutant proteins were either expressed from a transgene (M1–M3, M5–M9, M11–M12) or from endogenous su(Hw) mutant alleles (M4, M10). (C) The shown table summarizes the function associated with Su(Hw) ZF mutants. The four categories include in vitro DNA binding based on EMSA assays, in vivo DNA binding based polytene chromosome assays, gypsy insulator activity based on body, wing and bristle (y2, ct6, f1) phenotypes and female fertility based. The scale corresponds to ++++ = 75–100%, +++ = 50–74%, ++ = 25–49%, + = 5–24%, − = <5% of wild-type function.