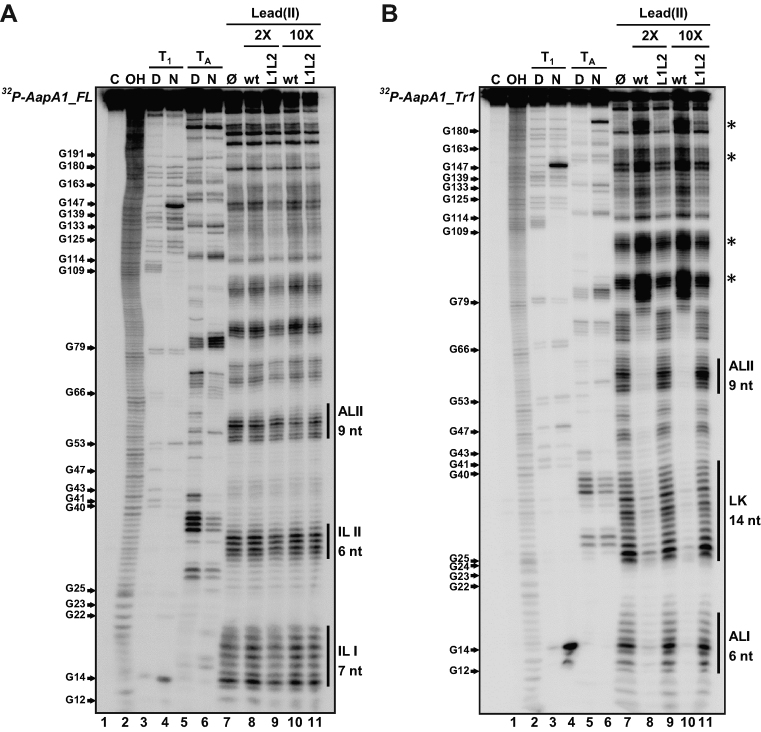
Figure 4.
Structure probing of (A) AapA1_FL and (B) AapA1_Tr1 RNAs in presence or absence of IsoA1. The secondary structure of each in vitro transcribed RNA was probed by submitting ∼0.1 pmol 32P- labeled RNA to partial enzymatic digestion either under native (N) or denaturing conditions (D) (RNase T1 cleaving single stranded G residues, lanes 3 and 4 ; RNase TA cleaving single stranded A residues, lanes 5 and 6). The interaction between AapA1 and IsoA1 was mapped using lead probing (lanes 7–11) in the absence (lane 7) or presence of either 2 or 10 times excess of wild-type IsoA1 (wt, lanes 8 and 10) or IsoA1 mutated in its apical loop (L1L2, lanes 9 and 11). Structure mapping, as well as secondary structures of IsoA1 wt and L1L2, are shown in Supplementary Figure S4. Untreated RNA (lane 1, denoted C) and partially alkali digested RNA (lane 2, denoted OH) served as control and ladder, respectively. Cleaved fragments were analyzed on an 8% denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Positions of all G residues are indicated relative to the transcription start site of the aapA1 gene (left of the gel). Single stranded regions involved in the 5΄ structural rearrangement are indicated by vertical black bars (right of the gel). The internal loops I and II (IL I, IL II) present in AapA1_FL are replaced by an apical loop (AL II) and a 14-nucleotides linker (LK) in AapA1_Tr1. Black stars on the right of the gel indicate other structural rearrangements observed following IsoA1 RNA binding.