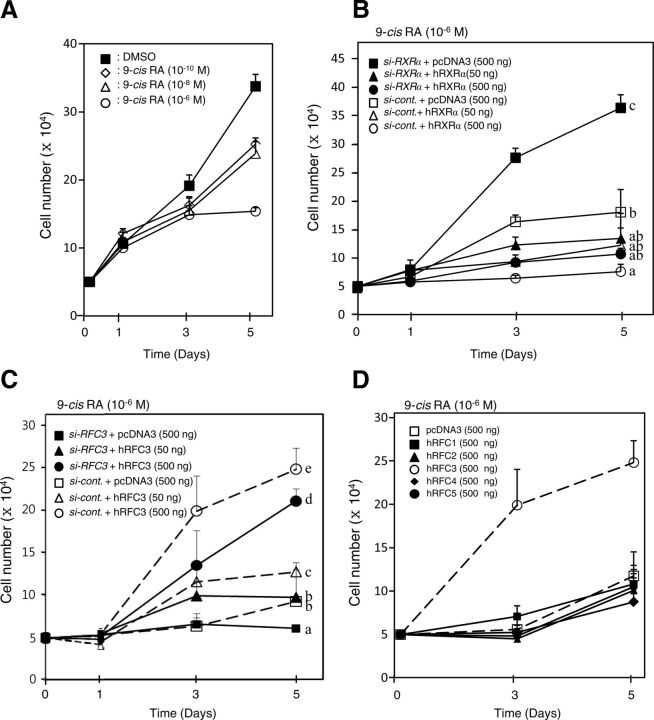
Fig. 6.
Knockdown of RXRα or overexpression of RFC3 restores proliferation of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells inhibited by 9-cis-RA. A, MCF-7 cells were inhibited by 9-cis-RA in a dose-dependent manner. The cells were plated at a density of 5 × 104 cells per 24-well plate culture and incubated for 5 d. At 1 and 3 elapsed days, 9-cis-RA was added to the culture medium. Aliquots of the cell suspension were placed on a hemocytometer, and the number of cells able to exclude trypan blue was counted under light microscopy at 1, 3, and 5 elapsed days. Cell numbers are expressed as the mean ± sd of three independent wells. B, Knockdown of human RXRα rescues MCF-7 cell proliferation suppressed by 9-cis-RA. MCF-7 cells were plated at a density of 5 × 104 cells as in A, and the cells were transfected with 0.8 μg siRNA-RXRα or siRNA-control, along with the indicated amount of the hRXRα expression vector. At 1 and 3 d after transfection, the cells were treated with 9-cis-RA (10−6 m). At 1, 3, and 5 d after transfection, the cell numbers were counted as in A. C, hRFC3 restores MCF-7 cell proliferation suppressed by 9-cis-RA. MCF-7 cells were transfected with 0.8 μg siRNA-RFC3 or siRNA-control, along with the indicated amount of hRFC3 expression vector. The cells were treated with 9-cis-RA (10−6 m), and the numbers of cells were counted as in A. D, hRFC3 specifically recovers proliferation of 9-cis-RA-treated MCF-7 cells. MCF-7 cells were transfected with RFC expression vector, as indicated, and then treated with 9-cis-RA and counted as in A. Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) among treatment groups at 5 d after transfection.