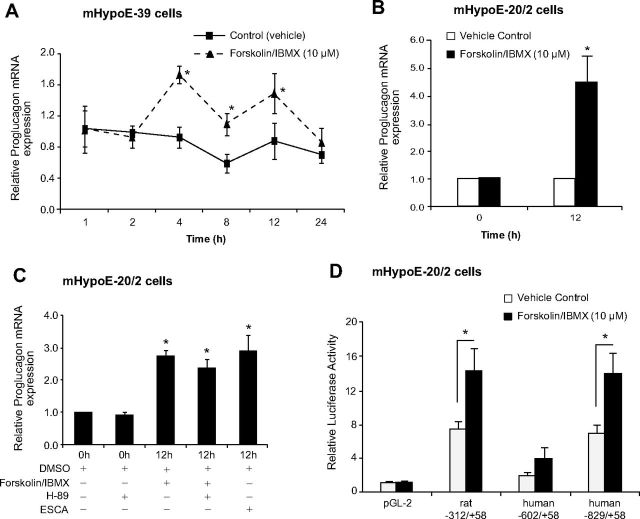
Fig. 7.
cAMP regulates proglucagon gene expression in the embryonic hypothalamic neuronal cells via activation of the Epac pathway. After overnight serum starvation, the mHypoE-39 (A) and mHypoE-20/2 (B and C) cells were exposed to vehicle, forskolin/IBMX (10 μm), or Epac pathway-specific cAMP analog ESCA (50 μm) over a 24-h time course. To determine the involvement of the PKA pathway in proglucagon mRNA regulation by cAMP, the mHypoE-20/2 neuronal cells were pretreated with a PKA inhibitor, H89 (1 μm), for 45 min followed by forskolin/IBMX (10 μm) treatment. Total RNA was extracted at the indicated time points and used as a template for real-time RT-PCR with primers specifically designed to amplify proglucagon mRNA. Proglucagon mRNA levels were quantified using the cycle threshold method and normalized to the internal control (γ-actin). All results shown are relative to corresponding control mRNA levels at each time point. For the transient transfection analysis, mHypoE-20/2 cells were transfected with proglucagon 5′ flanking plasmids or promoterless control plasmid pGL2 (D), incubated for 24 h, and then treated with vehicle or forskolin/IBMX (10 μm). Cells were harvested 12 h after treatment and a luciferase assay was performed. Data from the luciferase assay were normalized to protein concentration. All results are expressed as mean ± sem (n = 4 independent experiments). *, P < 0.05. Statistical significance was calculated by one- or two-way ANOVA.