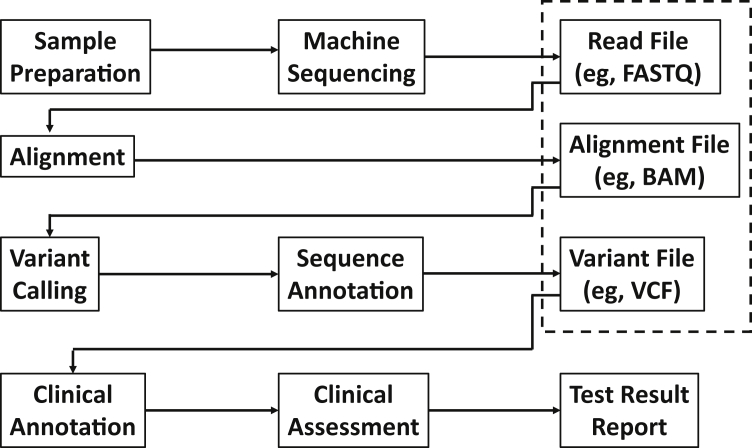
Figure 1.
Next-generation sequencing workflow and associated data files (designated with a dashed-line box). Machine sequencing of the patient sample produces a large number of short reads deposited in a file with associated quality scores (eg, FASTQ). These reads are aligned to a reference assembly or sequence and the results are deposited in an alignment file (eg, BAM). Variants are called and their properties relevant to the sequence (eg, type of variant) are annotated and deposited in the variant file [eg, variant call format (VCF)]. The data in the variant file are further analyzed to determine what findings are clinically relevant and reportable to the physician to inform medical decision making.