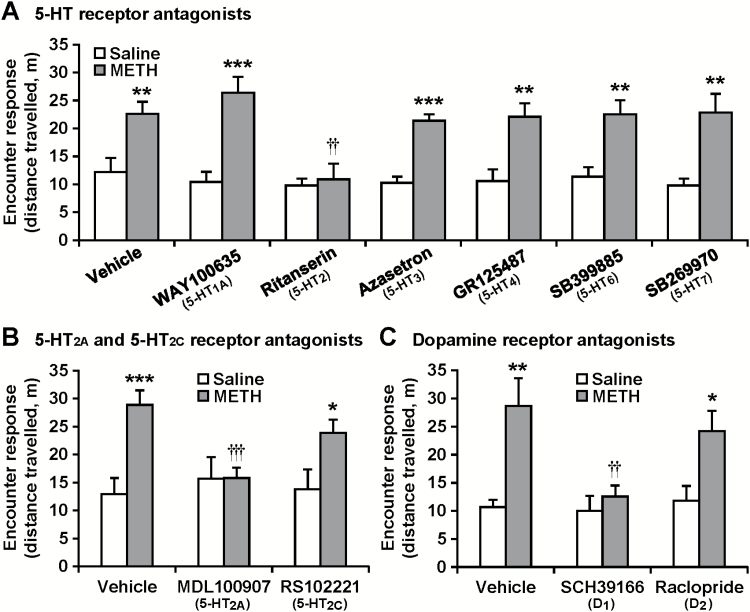
Figure 6.
Effects of serotonin (5-HT) and dopamine receptor antagonists on encounter-induced hyperactivity in methamphetamine (METH)-sensitized mice. The resident chronic METH- or saline-pretreated mice were injected (i.p.) with the 5-HT receptor subtype antagonists WAY100635 (1 mg/kg), ritanserin (3 mg/kg), azasetron (3 mg/kg), GR125487 (3 mg/kg), SB399885 (3 mg/kg), or SB269970 (1 mg/kg) (A), MDL100907 (1 mg/kg) or RS102221 (1 mg/kg) (B), the dopamine receptor antagonists SCH39166 (0.2 mg/kg) or raclopride (0.1 mg/kg) (C), or vehicle 30 minutes before the encounter with the intruder. Total distance travelled in the area near the partition during the 20-minute encounters was analyzed as an index of the encounter response. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of 12 mice/group. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, compared with saline-pretreated mice in each antagonist-treated group. ††P < .01, †††P < .001, compared with vehicle-injected METH-pretreated mice.