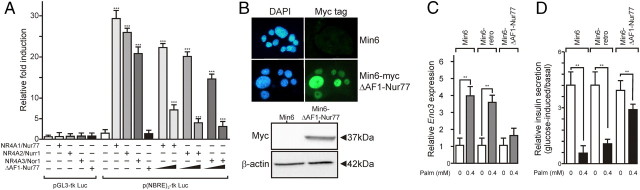
Fig. 5.
A transcriptionally defective Nur77 mutant partially blunts lipotoxic effects of palmitate. A, The ΔAF1-Nur77 mutant behaves as a dominant-negative transcription factor in Min6 cells. Min6 cells were transfected either with a control reporter gene (pGL3-tk Luc) or a NBRE-driven reporter gene [p(NBRE)3-tk Luc], with a fixed amount of an expression vector coding either for Nur77, Nurr1, or Nor1. A 5- or 20-fold stoichiometric excess of ΔAF1-Nur77 expression was also used where indicated. Luciferase activity was assayed 48 h after transfection and expressed relative to the basal luciferase activity detected in Min6 cells transfected with p(NBRE)3-tk Luc, which was set to 1. Data are presented as the mean ± sem. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc test and is displayed as *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005. B, Characterization of Min6 cells overexpressing a myc-tagged version of the dominant-negative, transcriptionally inactive Nur77 mutant. Naive or retrovirally transduced Min6 cells were stained for Myc-tag detection (upper panel), and whole-cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot to assess the molecular mass of the N-terminally truncated Nur77 protein (lower panel). C, Palmitate induction of enolase 3. Min6 or Min6 ΔAF1-Nur77 was treated with palmitate, and enolase 3 expression was monitored by RT-QPCR. Data are presented as the mean ± sem (n = 2) with basal level set to 1. Statistical significance was evaluated by a t test and is displayed as *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. D, Insulin secretion of Min6/ΔAF1-Nur77 cells. Min6 or Min6 ΔAF1-Nur77 cells were treated for 48 h with the indicated concentration of palmitate, and the insulin secretion was assayed as in panel A. Results are expressed as the ratio of the low-glucose to high-glucose insulin secretion. Data are presented as the mean ± sem (n = 2). Statistical significance was evaluated by a t test and is displayed as *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.