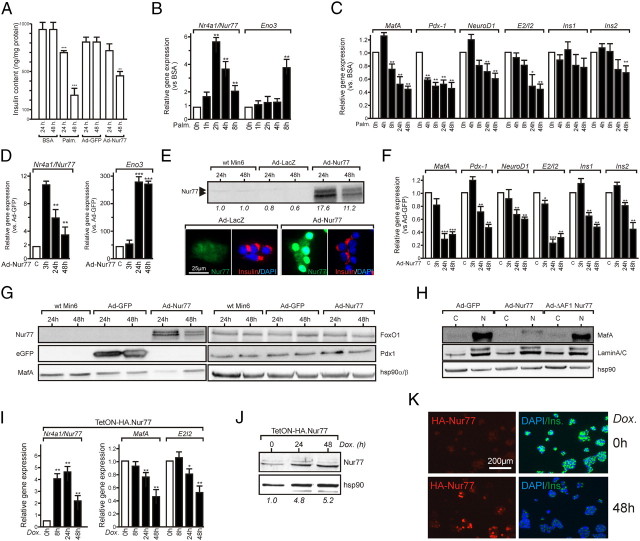
Fig. 6.
Nur77 regulates insulin synthesis. A, Min6 insulin intracellular content. After palmitate treatment or adenoviral transduction for the indicated times, cell layers were processed to extract and assay insulin. Data are presented as the mean ± sem (n = 3). Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc test and is displayed as *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005. B, Nur77 responsiveness to palmitate treatment. Min6 cells were treated with 0.4 mm palmitate for the indicated times, and gene expression levels were assayed by QPCR. Basal levels were arbitrarily set to 1. Data are presented as the mean ± sem (n = 3) and were analyzed as in panel A. C, Nur77 target genes expression after palmitate treatment. Min6 cells were treated for the indicated times, and gene expression was assayed and analyzed as in panel A. D, Adenoviral transduction of Nur77 elevates enolase3 expression. Min6 cells were transduced with Ad-Nur77, and gene expression was monitored and analyzed as in panel A. E, Nur77 protein expression level in transduced Min6 cells. Min6 cells were transduced with the indicated adenovirus, and the Nur77 polypeptide was detected by either Western blot (upper panel) or indirect immunofluorescence (lower panel). Data were quantified using the ImageQuant software. F, Nur77 target genes expression after adenoviral transduction. Min6 cells were transduced as in panel D, and data were collected and expressed as in panel A. G, Adenovirus-mediated expression of Nur77 decreases mafA expression. Whole-cell extracts were prepared 24 or 48 h after transduction with the indicated adenoviruses and analyzed by Western blotting. H, mafA is expressed in the nucleus. Cytosolic (C) and nuclear fractions (N) were prepared in conditions similar to panel G and analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-mafA, an anti-Nur77 (targeting the N terminus of Nur77), or anti-laminA/C and anti-hsp90, used as a marker for the nuclear fraction or for even loading, respectively. I–K, Nur77 equally represses insulin expression in the doxycyclin-dependent system TetON-HA.Nur77. I, Gene expression in TetON-Nur77 cells. Cells were treated by doxycyclin for the indicated time, after which total RNA was extracted and analyzed for its content in Nur77, mafA, and insulin pre-mRNA content (E2/I2). The abundance of each mRNA in the basal state was arbitrarily set to 1, and data are presented as the mean ± sem (n = 3). Data are presented as the mean ± sem (n = 3) and were analyzed as in panel A. J, Nur77 protein expression levels in the doxycyclin-dependent system TetON-HA.Nur77. Bands were quantified using ImageQuant software. K, Insulin intracellular content in the doxycyclin-dependent system TetON-HA.Nur77. Nur77 and insulin were detected by indirect immunofluorescence in noninduced (0 h) and after a 48-h doxycyclin treatment (48 h).