Fig. 4.
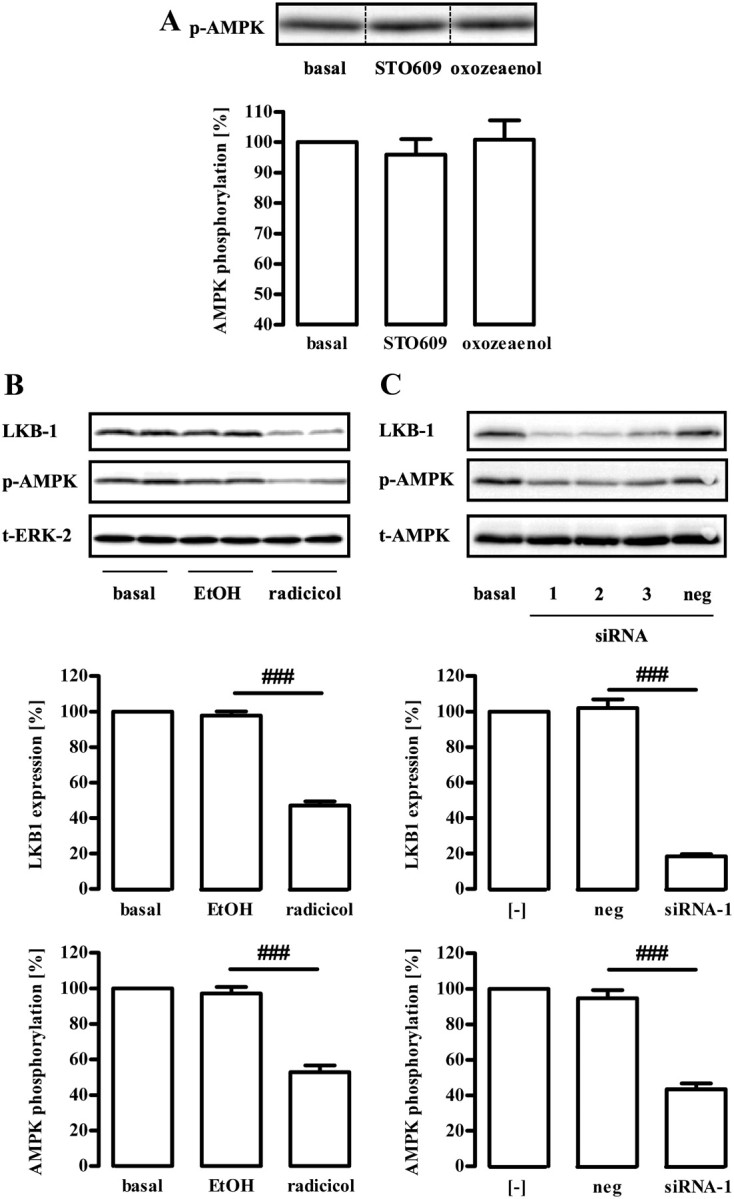
Role of LKB-1 for basal AMPK phosphorylation at Thr172. Approximately 400,000 GT1-7 cells were grown in six-well plates, serum starved for 20 h, and analyzed by Western blotting using a phospho-specific antibody against Thr172 of AMPK. A, Cells were treated for 30 min with the CaMKKβ inhibitor STO609 (1 μm) or the TAK-1 inhibitor oxozeaenol (500 nm), respectively. One representative blot is shown. The dotted line indicates grouping of different lanes from the same gel. B, Serum-starved cells were incubated with the Hsp90 inhibitor radicicol (10 μm) for 20 h or as a control with the carrier ethyl alcohol (EtOH) (1%). C, Cells were transfected with three distinct siRNA (1–3) designed to specifically down-regulate LKB-1 and one random siRNA (neg) by electroporation and serum starved for 20 h after 1 d of recovery. Samples were analyzed by Western blotting using an antibody either against AMPK-Thr172, LKB-1, ERK-2, or t-AMPK-α. One representative blot for each antibody is shown. Data of five (A) or four (B) independent experiments were compiled, normalized by setting basal values as 100%, and are shown in the bar graphs as the mean ± sem. A, Hashed signs indicate a significant (###, P < 0.001) difference between radicicol-treated and EtOH-treated cells or between siRNA-1 and the random siRNA in B.
