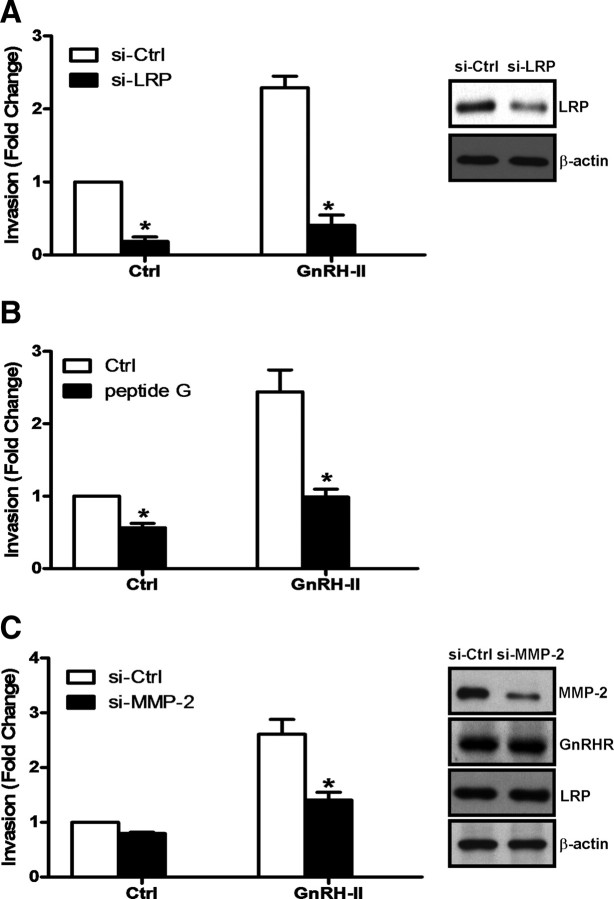
Fig. 8.
LRP and MMP-2 are key mediators of GnRH-II enhanced invasion in ovarian cancer cells. A, CaOV-3 cells were treated with 75 nm LRP siRNA (si-LRP) or 75 nm control siRNA (si-Ctrl) for 24 h, and with 10 nm GnRH-II for a further 48 h during an invasion assay. B, In parallel experiments, 1 μg of peptide G was preincubated with Matrigel-coated transwells for 30 min before invasion assay in the presence of 10 nm GnRH-II for 48 h. C, CaOV-3 cells were treated with 75 nm MMP-2 siRNA (si-MMP-2) or 75 nm control siRNA (si-Ctrl) for 24 h, before an invasion assay in the presence of 10 nm GnRH-II for 48 h. Results are expressed as mean ± sem of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 compared with control siRNA (si-Ctrl) in A and C or untreated control (Ctrl) in B. The efficiency of LRP siRNA and MMP-2 siRNA were verified by Western blot analysis of LRP (right panels in A and C). In parallel experiments, si-MMP-2–treated cells were harvested and protein extracts were subjected to Western blotting with antibodies against LRP, GnRHR, or β-actin as a normalization control.