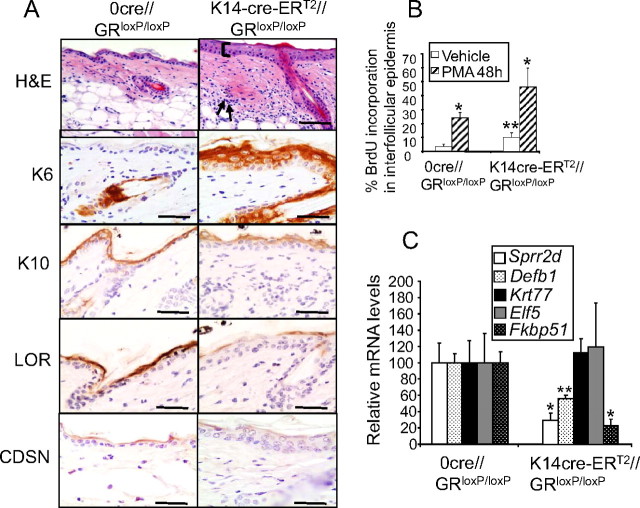
Fig. 6.
Alterations in proliferation, differentiation, and gene expression of K14-cre-ERT2//GRloxP/loxP mice. A, Impaired proliferation and differentiation of adult skin with keratinocyte-restricted GR inactivation. H&E staining of adult K14-cre-ERT2//GRloxP/loxP mice showed thickened epidermis (bracket) and a marked dermal infiltrate (arrows). Immunostaining using specific antibodies against keratin 6 (K6), keratin 10 (K10), loricrin (LOR), and CDSN shows abnormal epidermal proliferation and differentiation in the conditional knockout mice. Bars, 50 μm. B, Percentage of BrdU incorporation in adult interfollicular epidermis treated with vehicle or the phorbol ester PMA for 48 h. C, Gene regulation in the absence of GR in adult keratinocytes was determined by QPCR using the epidermis of adult conditional knockouts and control tail biopsies. Coincidences and divergences in gene regulation due to the lack of GR were found in adult vs. embryonic skin. Fkbp51, Sprr2d, and Defb1 mRNA levels were strongly repressed in K14-cre-ERT2//GRloxP/loxP mice whereas no changes in Krt77 or Elf5 transcripts were detected. Statistically significant differences were assessed by Student′s t test (*, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.005).