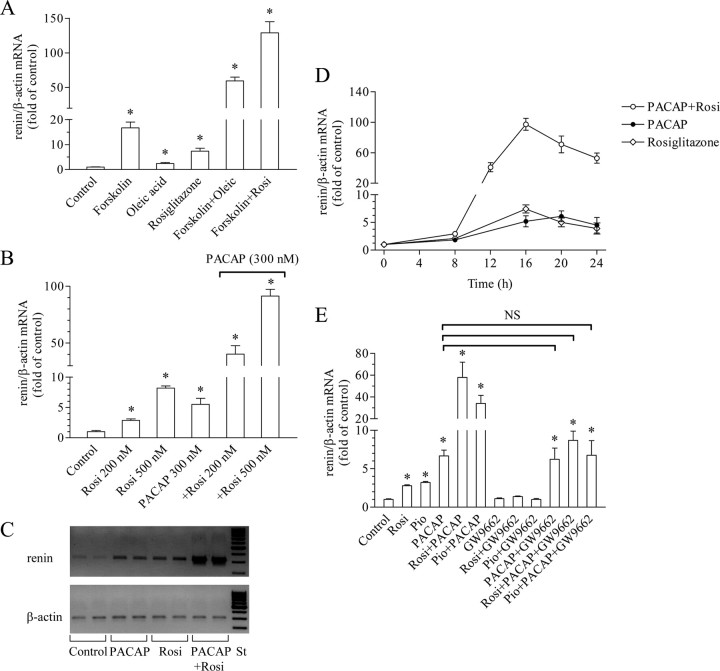
Fig. 1.
PPARγ agonists potentiate the cAMP-induced stimulation of renin gene expression. A, Effect of the PPARγ agonists oleic acid (250 μm) and rosiglitazone (500 nm) on the stimulation of renin gene expression by the direct AC activator forskolin (5 μm). B, Effect of the PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone (200 or 500 nm) on the stimulation of renin gene expression by the membrane receptor-binding AC activator PACAP (300 nm). C, Representative bands of amplified renin and β-actin cDNA fragments. Total RNA was isolated form Calu-6 cells incubated for 16 h as indicated (rosiglitazone was applied at 500 nm, PACAP at 300 nm). After reverse transcription, cDNA was amplified with the corresponding primers in real-time PCR. PCR was terminated in the linear phase of amplification, and the samples were loaded onto 2% agarose gel. St, Length standard. D, Time course of the effect of rosiglitazone (500 nm), PACAP (300 nm), or the combination of both on renin gene expression. E, The PPARγ antagonist GW9662 (1 μm) abrogates the potentiation of PACAP (300 nm)-induced renin gene expression by rosiglitazone (200 nm) or pioglitazone (1 μm). NS, Not significant. Renin and β-actin (internal control) mRNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR. Unless otherwise specified, Calu-6 cells were incubated with the indicated substances for 16 h. Control cells remained untreated throughout all experiments. Rosi, Rosiglitazone; Pio, pioglitazone. The data shown are means ± sem; *, P < 0.05.