Fig. 2.
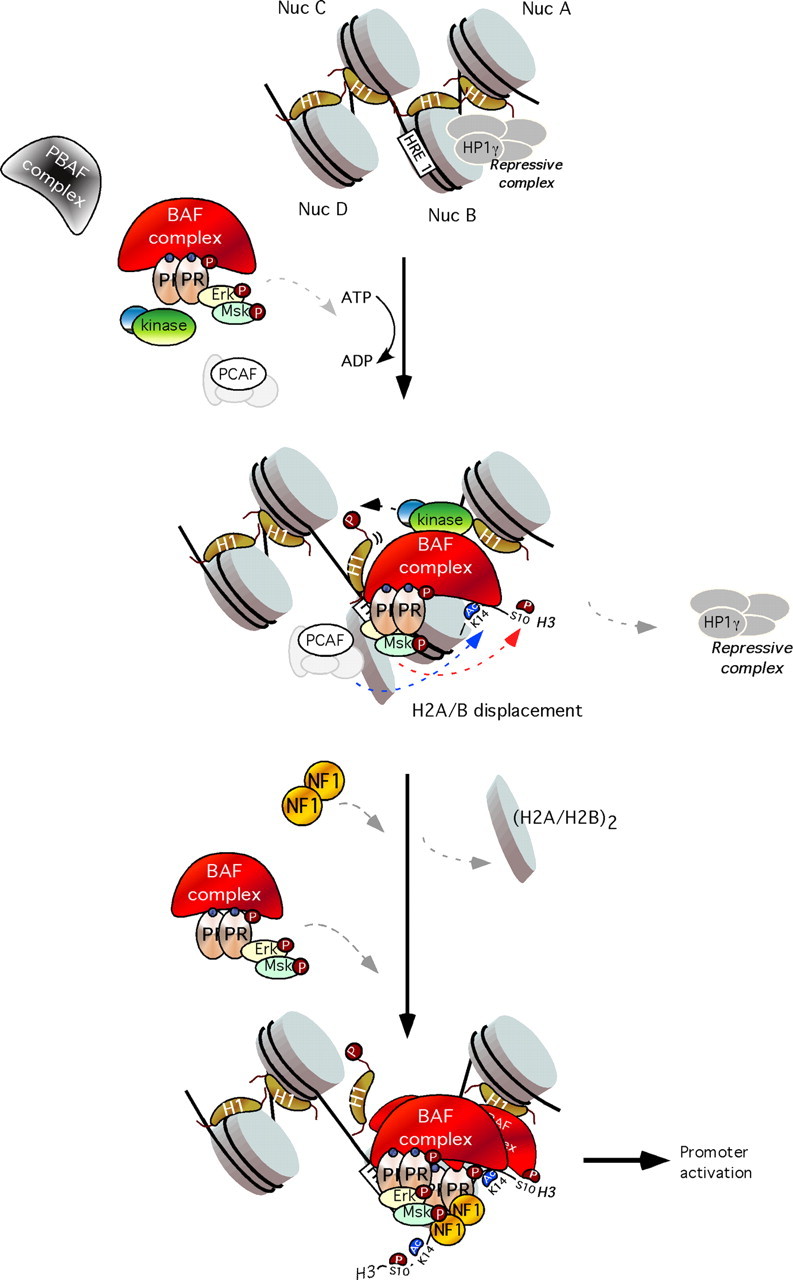
Model for the role of “PR activated complex” in chromatin. Top, In the uninduced state, an HP1γ-containing repressive complex is bound to the promoter, keeping it silent. Middle, Upon hormone induction, activated PR complexes bind BAF and P300/CRE-binding protein-binding protein-associated factor (PCAF) and recruit them to the exposed HRE1 on nucleosome B. This is followed by H3 phosphoacetylation and displacement of the repressive complex and histone H1. Bottom, The BAF complex, stabilized by PCAF-dependent H3K14 acetylation, catalyzes ATP-dependent H2A/H2B displacement and NF1 binding. This facilitates binding to the HREs 2 and 3 of further PR molecules with associated BAF, followed by other coactivators and the basal transcriptional machinery, including RNA polymerase II, leading to promoter activation. PBAF, Polybromo-associated BAF; Nuc, nucleosome.
