Fig. 2.
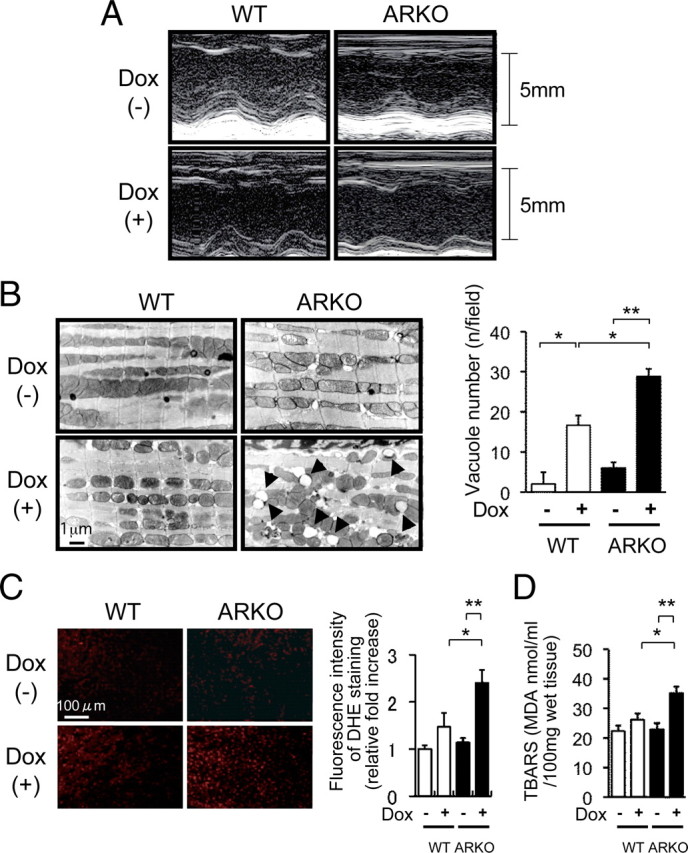
Left ventricular function, electron microscopic findings, superoxide generation, and lipid peroxidation after Dox administration in male WT mice and male ARKO mice. A, Representative M-mode echocardiogram of left ventricular wall motion. M-mode echocardiogram of the left ventriculum at 5 d after administration of the vehicle or Dox in male WT and male ARKO mice. Although there were slight extensional changes in left ventricular end-diastolic dimension (LVDd) and left ventricular end-systolic dimension (LVDs) of Dox-treated male WT mice, acute dilatation of LVDd and LVDs was markedly apparent in Dox-treated male ARKO mice. B, left panel, Electron microscopic findings of the left ventricular myocardium after administration of the vehicle or Dox in male WT and male ARKO mice. Accelerated vacuole formation of myocardial mitochondria was observed in Dox-treated male ARKO mice. Right panel, Quantitative analysis of vacuole number after administration of the vehicle or Dox in male WT (white bars) and male ARKO (black bars) mice. Values are expressed as means ± sem. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, n = 4–6 in each group. C, DHE bromide staining analysis after administration of the vehicle or Dox in male WT and male ARKO mice. D, Myocardial TBARS assay after administration of the vehicle or Dox in male WT (white bars) and male ARKO (black bars) mice. Values are expressed as means ± sem. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, n = 6–8 in each group.
