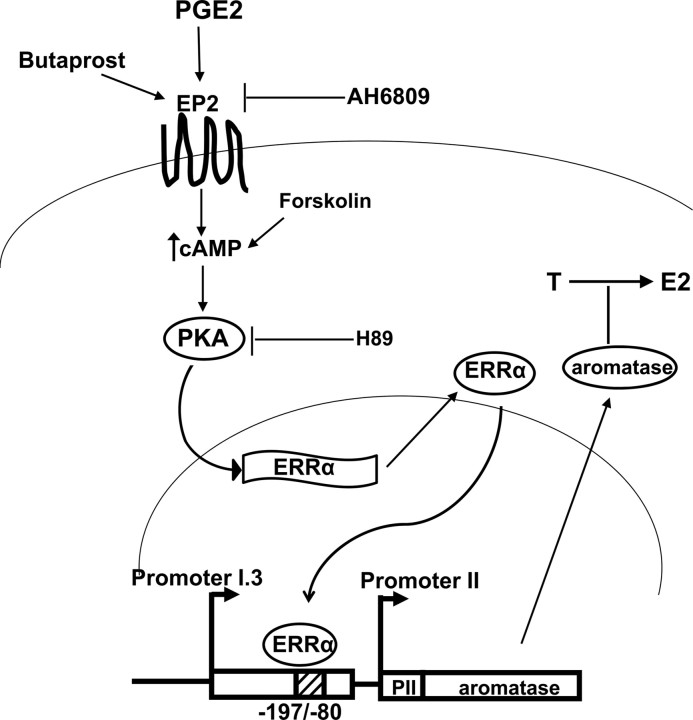
Fig. 7.
A schematic representation illustrating the relationship between PGE2, PKA, ERRα, aromatase and estrogen. PGE2 binds to PGE2 receptor EP2 located in the cell membrane of prostate stromal cells, leading to an increased production of cAMP. Then PKA is activated after binding to cAMP and results in up-regulation of ERRα expression. Both the EP2 agonist butaprost and cAMP activator forskolin mimics PGE2-induced ERRα expression in prostate stromal cells, which is blocked by the EP2 antagonist AH6809 and PKA inhibitor H89. Up-regulated ERRα interacts with the specific region (−197/−80) of the aromatase promoter, leading to transactivation of aromatase. The increased expression of aromatase then catalyzes the conversion from testosterone (T) into E2, leading to increased estrogen concentration.