Figure 1.
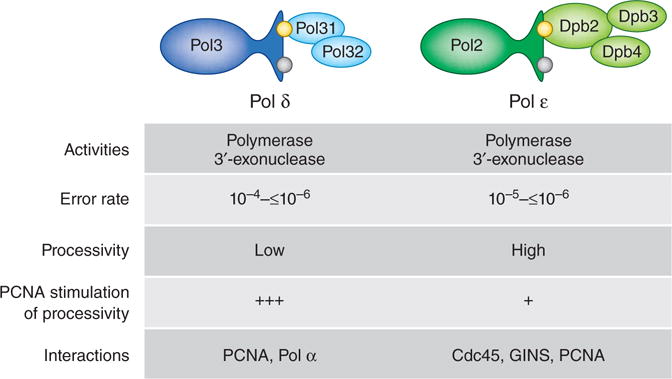
Comparison of DNA polymerases δ and ε. The four subunits of Pol ε (green) and the three subunits of yeast Pol δ (blue) are shown; a fourth subunit (p12) is present in the human enzyme. The catalytic (Pol3 and Pol2) subunits of both polymerases contain a 3′ exonuclease that can proofread replication errors to achieve the in vitro error rates shown above. The highest error rates are for single base deletions in long homonucleotide runs, which are proofread with low efficiency23. Consistent with a role in largely continuous leading-strand replication, Pol ε synthesizes DNA processively, i.e., without dissociating after nucleotide incorporation. Pol δ is highly processive only when assisted by PCNA. Proteins that interact with the individual polymerases are also listed.
