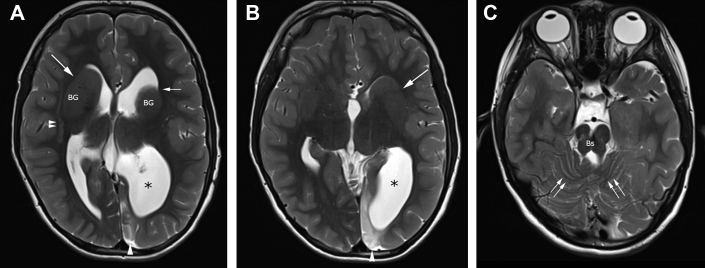
Fig. 1.
Axial T2-weighted brain MR imaging showing abnormal configuration of ventricles and abnormal internal capsule typical of tubulinopathy. Images at (A) level of the lateral ventricles and (B) third ventricle show a disproportionately large left lateral ventricle atrium (*), and frontal horns have an abnormal hooked morphology (small single arrow), associated with dysmorphic, bulbous basal ganglia (BG), and dysplasia of anterior limbs of internal capsules (long arrows). Linear band subcortical heterotopia [double arrowheads in (A)] is also evident. Left occipital parenchymal high signal (single arrowhead) is related to remote cortical insult, presumably vascular. (C) Image at the level of posterior fossa shows a hypoplastic brainstem (Bs) and cerebellar dysplasia evidenced by disorganized cerebellar folia (double arrows). MR, magnetic resonance.