Fig. 1.
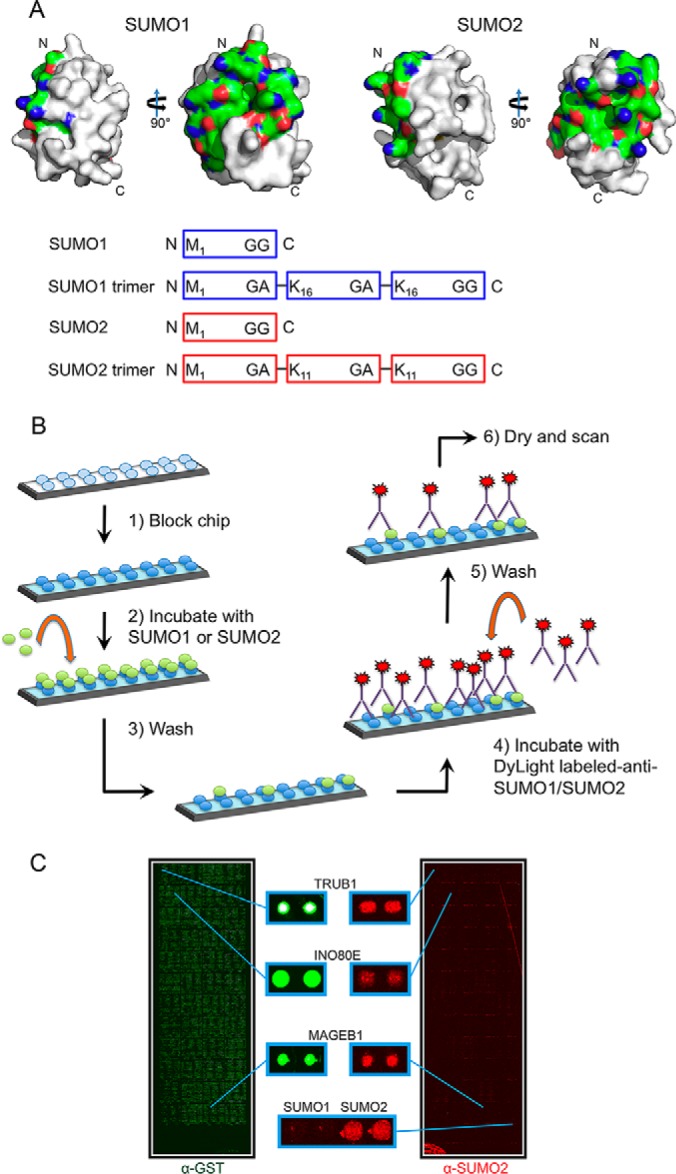
Design of protein microarray-based assay for identification of human SUMO binding proteins. A, (Top) SUMO1 and SUMO2 protein surfaces generated using MacPyMOL with previously reported crystal structures (SUMO1 PDB ID 2PE6 and SUMO2 PDB ID 4BKG). The surfaces corresponding to the first alpha-helix and second beta-strand for both SUMO1 and SUMO2 are shown in color (nitrogens are shown in red, oxygens in blue and carbons in green). This surface has been reported to be important for interactions with other proteins. (Bottom) Cartoon showing 4 probes that were used in our experiments. SUMO1 and SUMO2 monomer probes were based on the proteolytically processed (mature) forms of SUMO1 and SUMO2. The SUMO1 and SUMO2 trimer probes, described previously (Zhu 2008), were expressed as trimeric fusion proteins. B, Schematic of the SUMO-binding protocol used with the human proteome microarray. C, Representative microarray images showing human proteome microarray visualized with an antibody to GST, showing all proteins (left, in green), and an antibody to SUMO2 following a SUMO-binding experiment with the SUMO2 trimer (right, in red).
