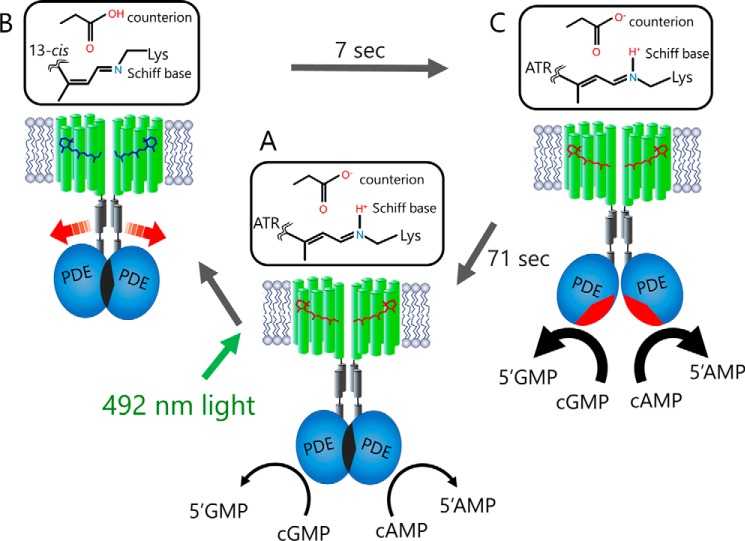
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the Rh-PDE activation mechanism. The model shows a putative Rh-PDE dimer. A, in the dark, Rh-PDE exhibits constitutive activity toward cGMP and cAMP, suggesting that the catalytic region is somewhat exposed to the cytoplasm in mammalian cells. B, upon absorption of blue-green light by the Rh domain, photoisomerization of the retinal chromophore from all-trans-retinal (ATR) to the 13-cis form produces the M intermediate with deprotonated Schiff base (Rh domain switch on), but the PDE domain has not changed yet (PDE domain switch off). C, next, the M intermediate decays to the parent spectral state in 7 s (Rh domain switch off), accompanied by the structural changes in the PDE domain (PDE domain switch on). The resulting increased enzymatic activity is turned off within ∼70 s (PDE domain switch off).