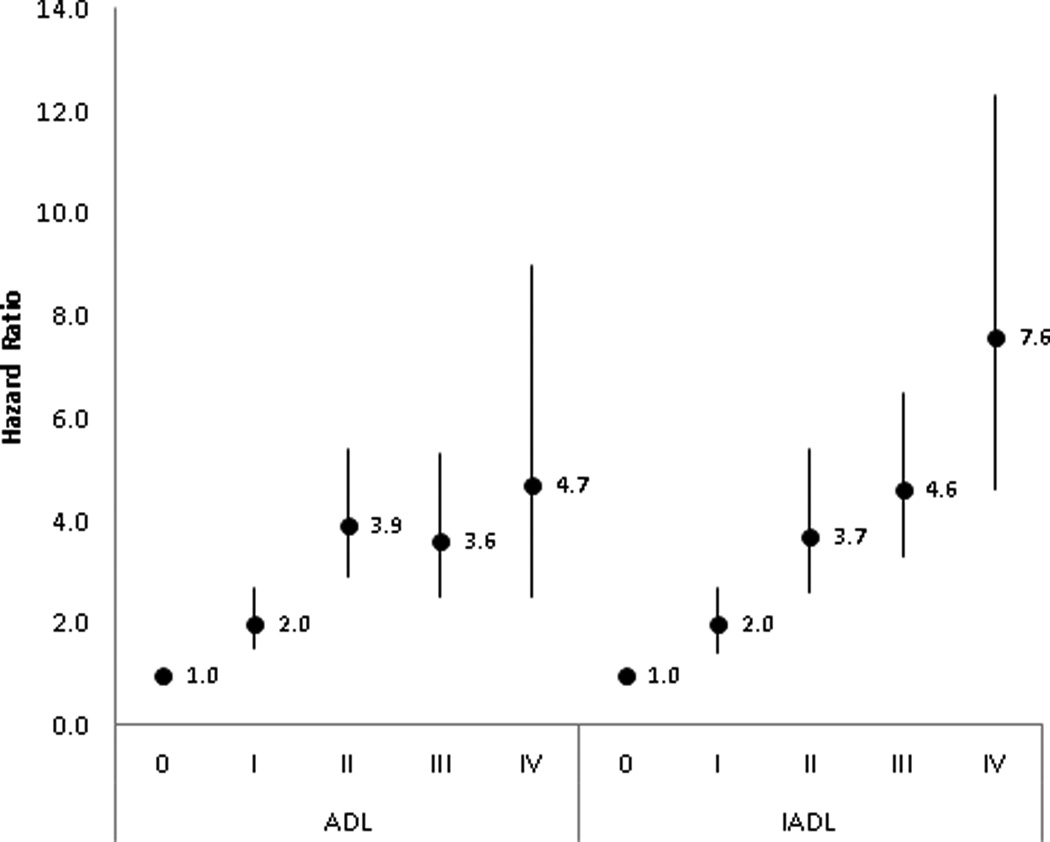
Figure 2. Association between Activity of Daily Living (ADL) and Instrumental Activity of Daily Living (IADL) Stages and Admission to Facilities Providing Long-term Care.
Key for Figure 2: reference = stage 0; Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) are from the fully-adjusted models (ADL or IADL stage in separate models, age, sex, race, education, living arrangement, dual eligibility, proxy status, and health conditions (Alzheimer’s disease, amputation, angina or coronary artery diseases, arthritis other than rheumatoid, broken hip, cancer other than skin, congestive heart failure, depression, diabetes type 1, 2, or other, emphysema/asthma/chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hardening of the arteries, heart rhythm disease, heart valve disease, hypertension, incontinence/catheterization, mental or psychiatric conditions, mental retardation, myocardial infarction, osteoporosis, paralysis, Parkinson’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and stroke).
The y-axis is the hazard ratios and the x-axis is the ADL or IADL stages.