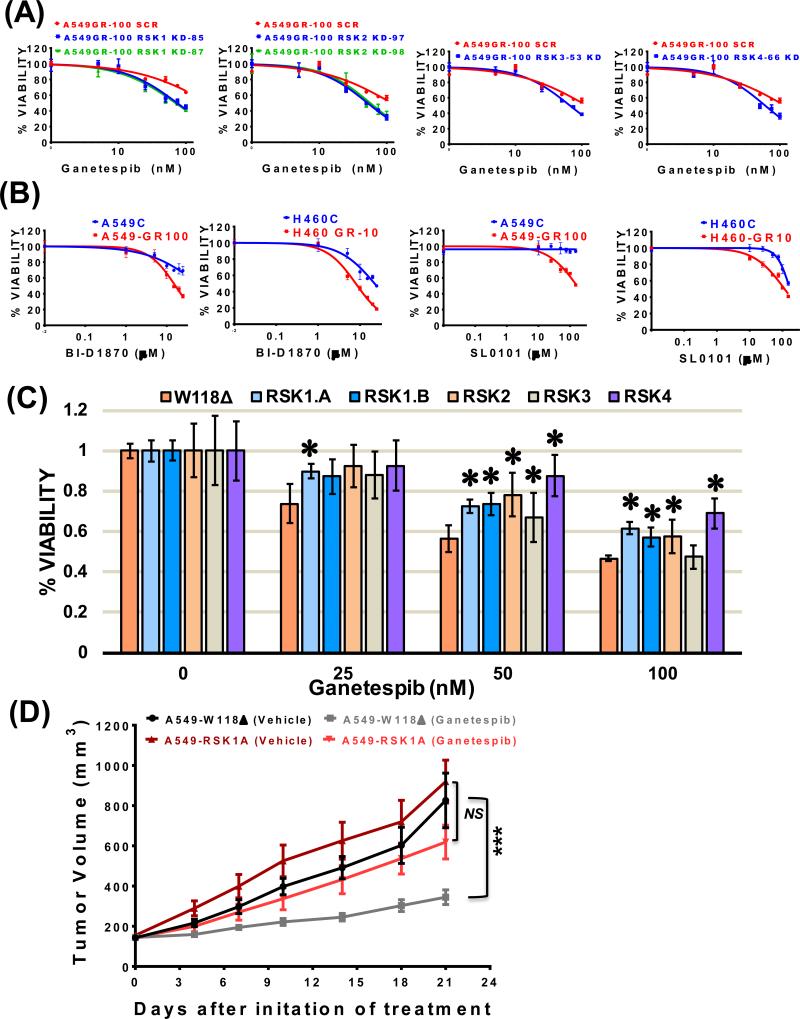
Figure 6. Ganetespib resistant cells are dependent upon p90RSK signaling, and overexpression of an individual p90RSK isoform is sufficient to induce ganetespib resistance.
(A) Individual p90RSK isoforms were silenced in A549-GR100 cells by expressing specific shRNA and percent viability was measured by MTS assays after 72 hours treatment with increasing concentrations of ganetespib. A549-GR100 cells expressing scramble shRNA (SCR) were used as a negative control. (B) Percent viability of A549 and H460 GR cells in comparison to control parental cells after a 72 hours of treatment with the pan-RSK inhibitors, BI-D1870 (0 – 25 μM) (left) and SL0101 (0 – 150 μM) (right) was determined by MTS assay. (C) p90RSK isoform specific ORFs were individually expressed in A549C parental cells and percent viability were assessed by MTS assays after 48 hours treatment with specific ganetespib doses (0, 25, 50 and 100 nM). A549C cells expressing empty vector – W118Δ was used as a negative control. Bars represent the mean percent cell viability (± SD) relative to the mean of control cells. Each cell type in each experiment included 4 replicates. Statistical significance by paired student t-Test are denoted as *, p < 0.05. (D) Ganetespib induced tumor regression was compared between control A549 xenografts arms either overexpressing empty vector W118Δ or the ORF of p90RSK-1A isoform. Tumor growth curves represent mean tumor volume (± SEM). N = 7 mice per treatment arm, except for W118Δ receiving ganetespib (N = 8). Linear contrasts in a random intercept linear mixed model indicate a greater treatment group difference in the W118Δ model (86% greater doubling time with ganetespib treatment) than for RSK1A (12% greater doubling time) (Wald ***, p < 0.001). NS = Not Significant.