Fig. 1.
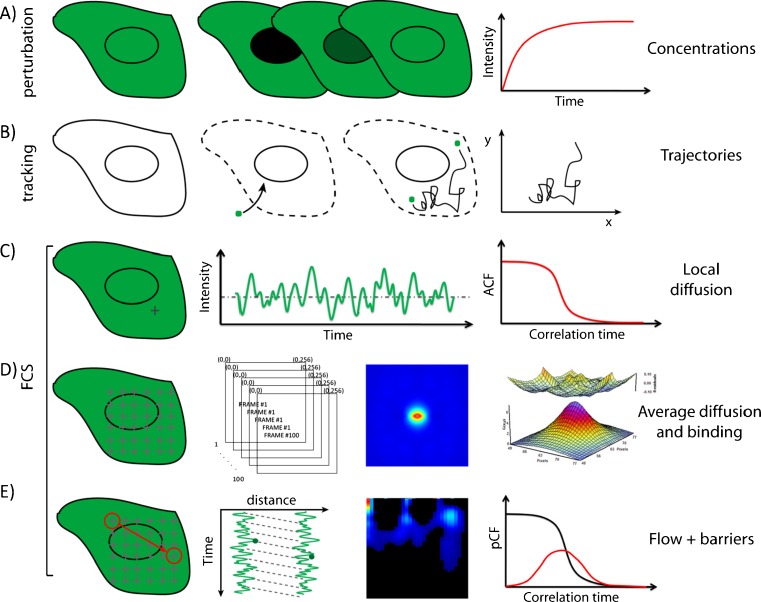
Comparison of the different methods available to probe intracellular diffusion. a FRAP is an ensemble measurement that provides temporal information on the recovery of the concentration of molecules without knowledge of where the fluorescence recovery originates from. b SPT requires purification, labeling and microinjection of the molecule of interest into cells; furthermore, a high statistic is needed to recover the molecular trajectories accurately. c The information obtained by the classical single-point FCS analysis is intrinsically local (one point at a time can be sampled in the cell). d RICS is a spatial temporal correlation method that takes into account how the cellular environment tested interacts with the molecules of interest, as well as what causes the net rate of molecular transport observed. Given the symmetry of the RICS correlation function, however, the direction of the flow or the behaviour of molecules at large distance cannot be determined. e The pair correlation method can measure the directionality of molecular flow by correlation the fluctuations at an arbitrary pair of points in the sample. By doing this, it is sensitive to the presence of barriers and/or obstacles to molecular diffusion