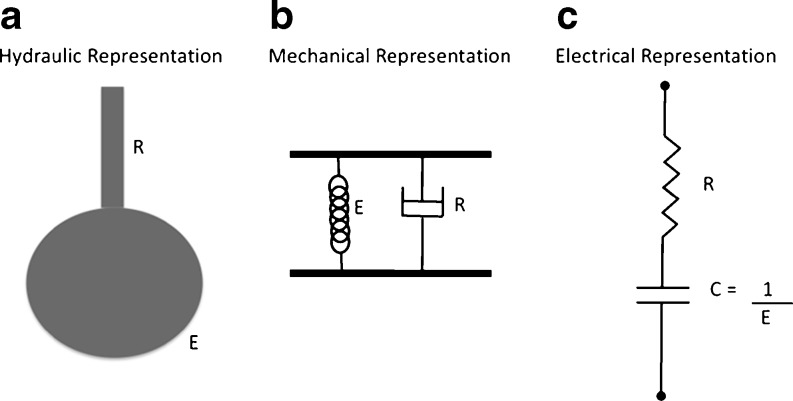
Fig. 2.
Representation of respiratory system considering the linear single-compartment model. Hydraulically (a) this model lung can represented by a balloon sealed over the end of a pipe. Mechanically, the association of a spring and a dashpot in parallel describes this model (b). The electrical analog consists of a serial association of a resistor and a capacitor (c). Note that the pipe (R) in the hydraulic representation is equivalent to the dashpot and the electrical resistor in the mechanical and electrical analog, respectively. The same can be observed with the balloon (E), which is represented by a spring or a capacitor, respectively. This analogy is valid when the airway pressure is equivalent to the force or tension and when flow is equivalent to velocity or current in the mechanical and electrical analogs, respectively. Thus, all representations are equivalent, and their constitutive equations are identical. This peculiarity stems from the impedance or indirect analogy used throughout this article