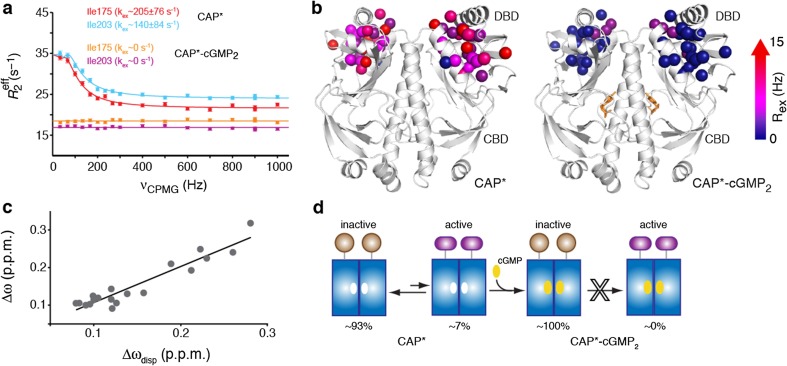
Fig. 2.
a Relaxation dispersion profiles of 13C side-chain methyls of representative CAP-T127L/S128I (CAP*) DBD residues in the apo and cGMP-bound form. b Enhanced R 2 relaxation rate (R ex) values of CAP* and CAP*–cGMP2. c Correlation between the 13CH3 Δω and Δωdisp chemical shifts of selected DBD residues. d CAP* interconverts between a ground state, which adopts the inactive conformation and is 93 % populated, and an excited state, which adopts the active conformation and is only ∼7 % populated. cGMP binding to CAP* results in the suppression of the active conformation through an allosteric mechanism. Figure reproduced from Tzeng and Kalodimos 2013