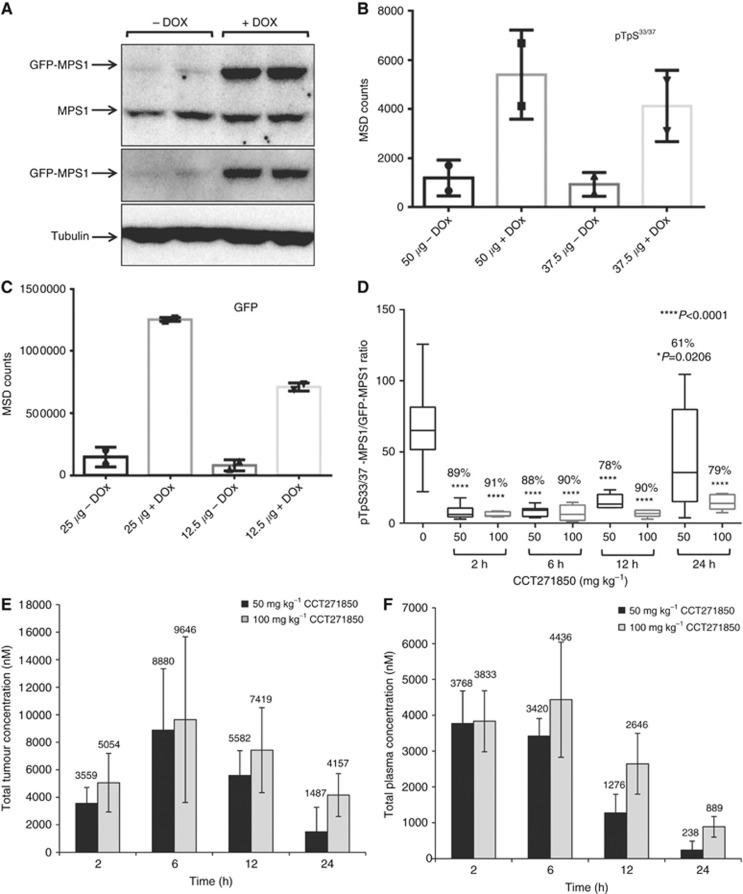
Figure 4.
Development of a PD biomarker assay for measuring direct inhibition of MPS1 in DLD1 GFP-MPS1 Dox-inducible xenografts.(A) Five million DLD1 cells, stably expressing Dox-inducible GFP-MPS1, were used to grow tumours in athymic mice. Mice were dosed with ∼6 mg of Dox per day for 3 days. Tumours were lysed and equal amount of protein was used for immunoblotting with GFP and MPS1 antibodies. (B) MSD assay for detection of MPS1 phosphorylation in xenograft tumours. Cell lysates (37.5 and 50 μg) from non-induced and induced tumours were used for MSD assay with pTpS33/37 antibodies. (C) Two concentrations (12.5 and 25 μg) of cell lysates were also used for MSD with GFP antibodies. (D) PK/PD studies in DLD1 GFP-MPS1 Dox-inducible xenografts treated with CCT271850. Mice bearing bilateral DLD1 (GFP-MPS1 Dox inducible) xenografts were placed on Dox diet for 3 days (∼6 mg/day). Twenty-four hours prior to harvest, mice were given a single 10 mg oral gavage bolus of Dox, followed by a single dose of 50 or 100 mg/kg of CCT271850. Tumours and plasma samples were collected at 2, 6, 12 and 24 h after CCT271850 dosing and followed with PK and PD examination. Samples were lysed and analysed by MSD for pTpS33/37 and GFP. Ratio of phospho-MPS1 (pTpS33/37)/Total-MPS1 (GFP) in tumour samples at various time points after 50 and 100 mg/kg CCT271850 dosing was calculated. Concentration of CCT271850 in tumours (E) and plasma (F) was measured.