Fig. 2.
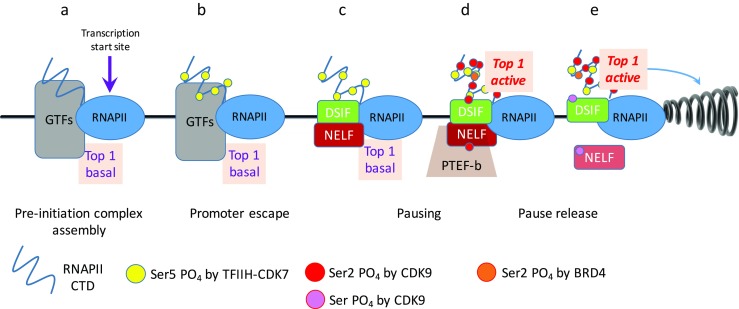
The transcription machinery actively manages topoisomerase activity. General transcription factors (GTFs: TFIIA, B, D, E, F, H) assemble into pre-initiation complexes. Negative elongation factor (NELF) and DRB-sensitivity inducing factor (DSIF) are complexes that are recruited to promoters that cause transcription to pause or to resume elongation, respectively, depending on their phosphorylation status. Positive transcription elongation factor b (PTEB-b) is the CDK9–cyclin T complex that phosphorylates serine 2 (Ser 2) and other targets, including DSIF and NELF. a Pre-initiation complexes assembled at start sites from multiple components include minimally active topoisomerase 1 (Top1); Top1 catalysis is not required for transcription initiation. The carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of the RNAPII–CTD complex is at this stage hypophosphorylated. b The kinase activity of TFIIH, CDK7 phosphorylates Ser 5 (yellow circles PO4-Ser 5,) contributing to promoter escape after nucleotide +8. Slow nascent transcription continues until point c, at which the recruitment of DSIF and NELF occurs during pausing. d At this stage Ser 2 is phosphorylated throughout the CTD (red circles PO4-Ser 2), as are DSIF and NELF, by the CDK9 subunit of PTEF-b (pink circles), and selective Ser 2s in the carboxyl terminal half of the CTD are phosphorylated by bromodomain chromatin factor 4 (BRD4; orange circles). e BRD4-phosphorylated CTD activates Top1 catalytic activity, removing torsional stress and allowing elongation to proceed
