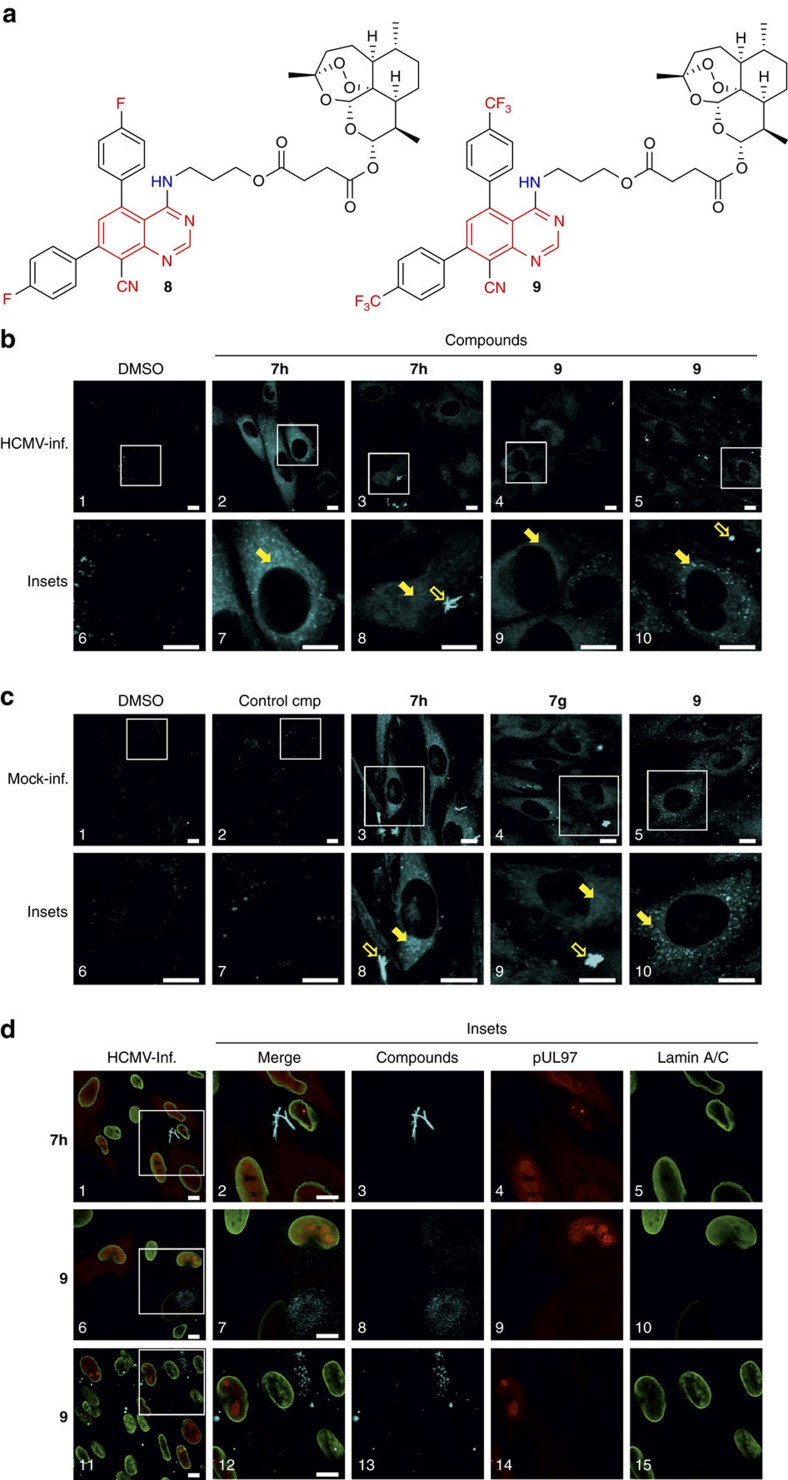
Figure 7. Microscopy-based visualization of cellular uptake of fluorescent quinazoline compounds.
(a) Artesunic acid–quinazoline hybrids 8 and 9. (b–d) Compounds 7h, 7g and 9 were analysed for properties of fluorescence imaging using confocal laser-scanning microscopy. HFFs were cultivated in six-well plates on cover slips and were either directly incubated with compounds by addition to the culture media for 20 h (c) or were added after HCMV infection (b,d; compound addition at 50 h post infection, fixation and analysis of cells 20 h later; scale bar, 10 μm). The chosen concentrations were 10 μM for compounds 7h, 7g and 9, or 1 μM for compound 9 in panels 4, 9 (b), panels 5, 10 (c) and panels 6–10 (d), referring to the compounds' EC50 values of anti-HCMV activity (see Table 1). The depicted images are representative for three independent experiments. Lack of mycoplasm contamination was verified by routine 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining. General procedures of cell fixation, indirect immunofluorescence staining of proteins (d) and microscopic analysis have been described elsewhere36,37.