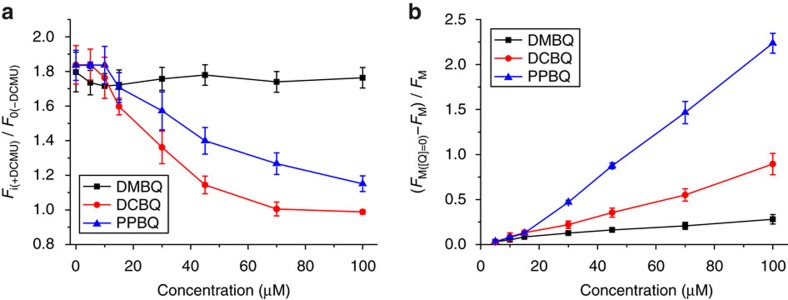
Figure 2. Ability of three quinone derivatives to deplete electrons from QB°− and/or PQ2− in the WT strain using chlorophyll fluorescence analysis.
(a) Effect of quinone derivatives on the ratio of initial fluorescence in the presence of 10 μM DCMU (Fi) to that in its absence (F0) (mean±s.d.; n=3). Addition of DCMU induces a rise of the initial fluorescence level that reflects the residual electron accumulation in the QB site or the plastoquinone pool in the dark. (b) Stern–Volmer plot of the maximum fluorescence yield (FM) showing the fluorescence quenching effect of exogenous quinones (mean±s.d.; n=3). FM([Q]=0) represents the FM value in the absence of quinones.