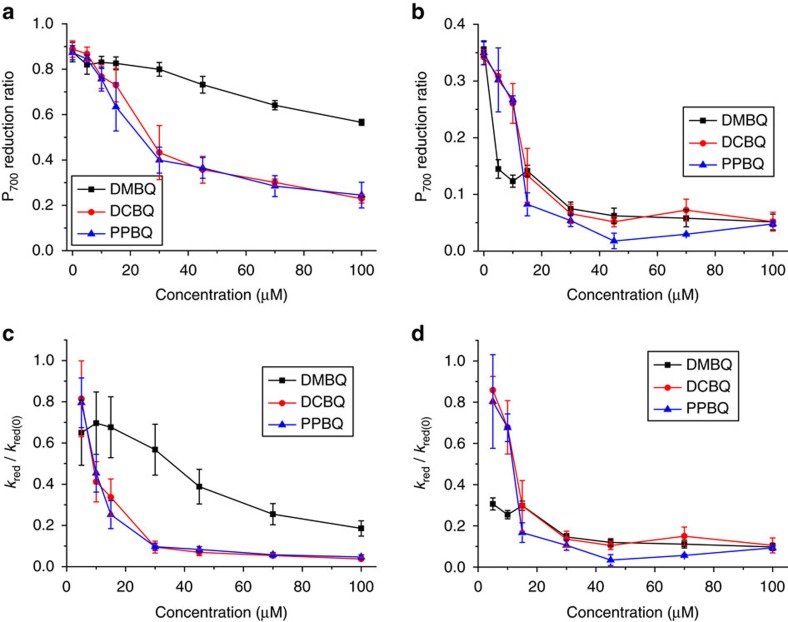
Figure 3. Efficiency of electron extraction for three quinone derivatives in the WT strain using light-induced absorbance changes of P700.
(a) P700 reduction ratio as a function of exogenous quinone concentration (mean±s.d.; n=4). P700 redox states were estimated from the absorbance changes at 705−730 nm. The P700 reduction ratio was calculated as 1 minus the oxidation level reached after a 10 s illumination (26 μmol photons m−2 s−1) over the level of full P700+ oxidation after a saturating light pulse. Decreases in the P700 reduction ratio indicate a reduced electron flux towards P700+ in the presence of exogenous quinones. (b) P700 reduction ratio as a function of exogenous quinone concentration in the presence of 10 μM DCMU (mean±s.d.; n=3). (c,d) P700 reduction rate (kred), normalized to the rate measured in the absence of quinones (kred(0)), as a function of exogenous quinone concentration, derived from the data of (a,b), respectively. The normalized kred/kred(0) ratio is particularly useful to compare strains or conditions that have different basal levels of P700 reduction ratio, as seen here after DCMU treatment.