Fig. 1.
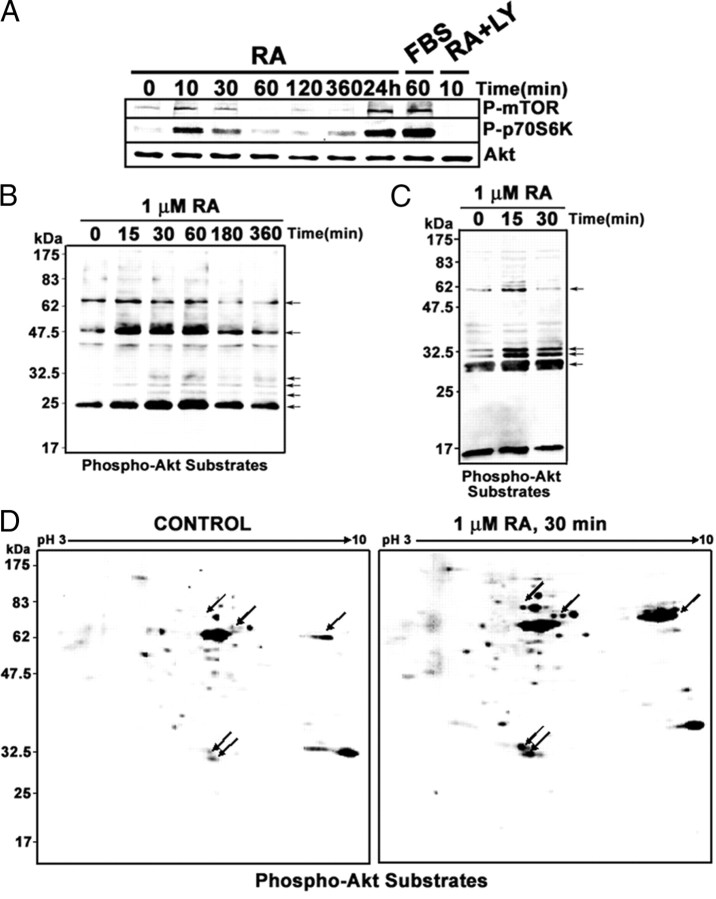
RA treatment of neuroblastoma cells results in activation of downstream components of the PI3K-signaling pathway. A, RA-induced activation of mTOR and p70S6 kinases. SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells were treated with RA (1 μm) for the times indicated, and total cell extracts were prepared. For comparison, we included an experiment in which cells were serum starved for 18 h and stimulated with 10% FBS for 30 min (lane labeled “FBS”). In addition, the extract from cells treated simultaneously with LY294002 (10 μm) and RA for 10 min was also included. The phosphorylation state of mTOR and p70S6 kinases was analyzed by Western blot with specific antibodies against the phosphorylated forms of the kinases (P-mTOR and P-p70S6). The filter was reprobed finally with antibodies against total Akt (AKT). Each lane contains 30 μg of total protein. B, RA-induced phosphorylation of Akt substrates. SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells were treated with RA (1 μm) for the times indicated, and total cell extracts were prepared. Each lane contains 30 μg protein from whole-cell extracts. The phosphorylation state of Akt substrates was analyzed by Western blot with specific antibodies against phosphorylated Akt recognition site. Arrows show several RA-induced bands. C, RA-induced phosphorylation of Akt substrates in the nucleus. SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells were treated with RA (1 μm) for the times indicated in the figure, and nuclear extracts were prepared. Each lane contains 30 μg protein from nuclear extracts. The phosphorylation state of Akt substrates was analyzed by Western blot with specific antibodies against phosphorylated Akt recognition site. Arrows show several RA-induced bands. D, RA-induced phosphorylation of nuclear Akt substrates in 2DE-Western blots. Each gel contains 30 μg nuclear protein from cells treated with RA (30 min, 1 μm) or vehicle (Control). The phosphorylation state of Akt substrates was analyzed by 2DE-Western blot with specific antibodies against phosphorylated Akt recognition site. Arrows show prominent spots the signal of which is increased by RA treatment. LY, LY294002.