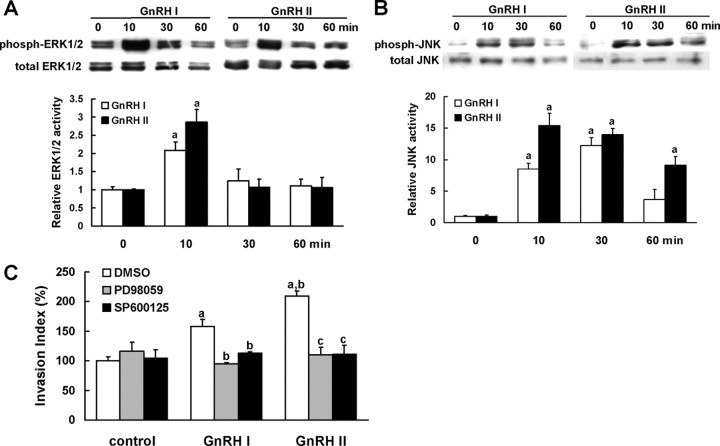
Fig. 3.
Activities of ERK1/2 and JNK are necessary for GnRH I- and GnRH II-induced EVT cell invasion. A and B, The EVTs were serum starved (>18 h) and then treated with 100 nm GnRH I or GnRH II for 10, 30, and 60 min, respectively. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (A) or JNK (B) was determined by Western blot with specific antibodies. The total amount of ERK1/2 or JNK was reprobed, and the relative density of phosphorylated ERK1/2 or JNK was normalized to total values of ERK1/2 or JNK, respectively. C, After 30-min pretreatment with vehicle (0.1% DMSO), PD98059 (10 μm, an ERK1/2 inhibitor), or SP600125 (10 μm, a JNK inhibitor), the EVTs were treated with GnRH I or GnRH II (100 nm), and the invasive capacity were analyzed by invasion assay. The data derived from at least three separate sets of experiments were standardized to the corresponding control, and the statistical results are presented in the column graphs. a, P < 0.05 vs. control; b, P < 0.05 vs. treatment with GnRH I alone; c, P < 0.05 vs. treatment with GnRH II alone.