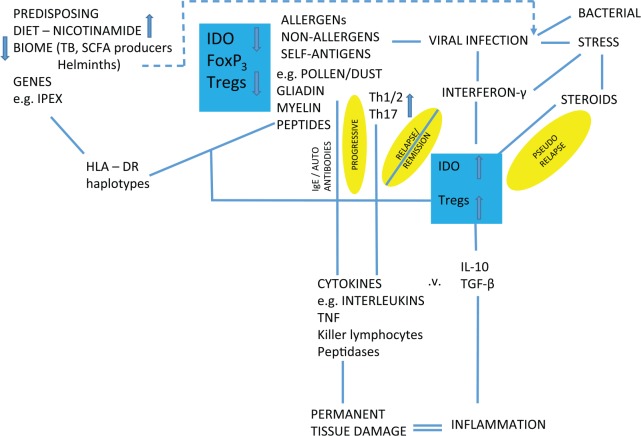
Figure 10.
Predisposing phenotype for inflammatory disease driven by high nicotinamide in diet leads to reduced IDO activity. The more immediate triggers to these diseases and the disease process itself may sometimes lead to the apparent paradox of induced IDO as a compensation that may exacerbate or mitigate the disease. Lack of early infections or allergens may be ultimate causes but can act later as proximate triggers. IDO indicates indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.