Fig. 6.
P-TEFb-Binding and GR Binding Are Separable for HEXIM1
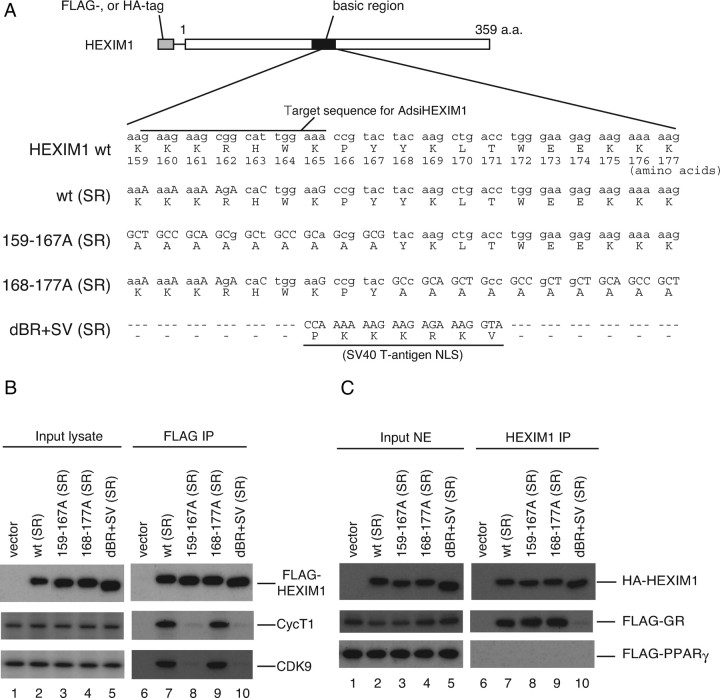
A, Schematic illustration of wild-type (wt) and mutant HEXIM1 used in this study. BR encompassing 150–177 amino acids are depicted as a solid box. Numbers depict positions of amino acids. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences in the BR are shown. Substitutions of nucleotides are shown in uppercase letters. wt (SR) and 168–177A (SR) have nucleotide substitutions in the target nucleotide sequence for AdsiHEXIM1 without affecting original amino acid sequence. 159–167A (SR) and dBR+SV (SR) are resistant to AdsiHEXIM1 by nature. B, HeLa cells were cotransfected with empty vector or expression plasmids for indicated FLAG-tagged mutant HEXIM1. Whole-cell lysates were prepared and subjected to FLAG-affinity purification as described in Materials and Methods. Western blot analysis of input lysates (lanes 1–5) and affinity-purified fractions (lanes 6–10) were performed using anti-FLAG peptide, anti-CycT1, and anti-CDK9 antibodies. C, COS7 cells were cotransfected with empty vector or expression plasmids for indicated HA-tagged mutant HEXIM1 along with either FLAG-tagged GR (middle panel) or FLAG-tagged PPAR γ (lower panel) expression plasmid. Cells were treated with 100 nm DEX (middle panel) or 100 nm TGZ for 2 h. Nuclear extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with anti-HEXIM1 antibodies. Western blot analysis of input extracts (lanes 1–5) and immunoprecipitated fractions (lanes 6–10) were performed using anti-HA peptide and anti-FLAG peptide antibodies. a.a., Amino acids; IP, immunoprecipitation; NE, nuclear extract; NLS, nuclear localization signal.