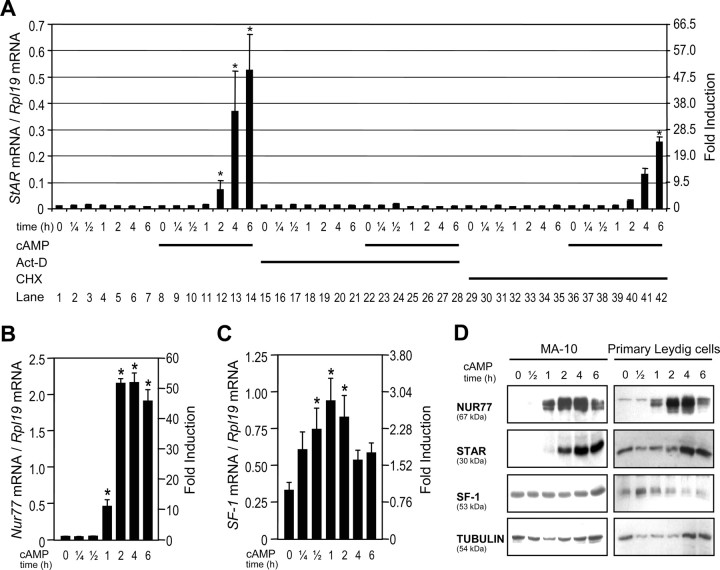
Fig. 1.
cAMP-Dependent Induction of Nur77 Precedes that of StAR
A, cAMP-induced StAR expression requires de novo protein synthesis. MA-10 Leydig cells were treated with (Bu)2-cAMP (0.5 mm), Act-D (8 μm), and CHX (25 μm) individually or in combination for the indicated times, and total RNA was isolated and used in quantitative real-time PCR using primers specific for StAR cDNA as described in Materials and Methods. B and C, MA-10 cells were treated with (Bu)2-cAMP (0.5 mm) as indicated, and expression of Nur77 (B) and SF-1 (C) was determined by real-time PCR. Results were corrected with the Rpl19 cDNA. Results are the mean of three individual experiments performed in duplicate (±sem). An asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference from the respective controls. D, Several experiments were performed where MA-10 and rat primary Leydig cells were treated with 0.5 mm (Bu)2-cAMP as indicated. For detection of NUR77 and SF-1, nuclear extracts (because of location in the nucleus) were prepared, whereas for StAR detection (because of location in mitochondria), whole-cell extracts were used. Western blots were done as described in Materials and Methods, and tubulin was used as a loading control. In the representative data shown here, the experiment to detect NUR77 was run separately from the other markers. However, all experiments were repeated at least three times and produced identical results.