Fig. 8.
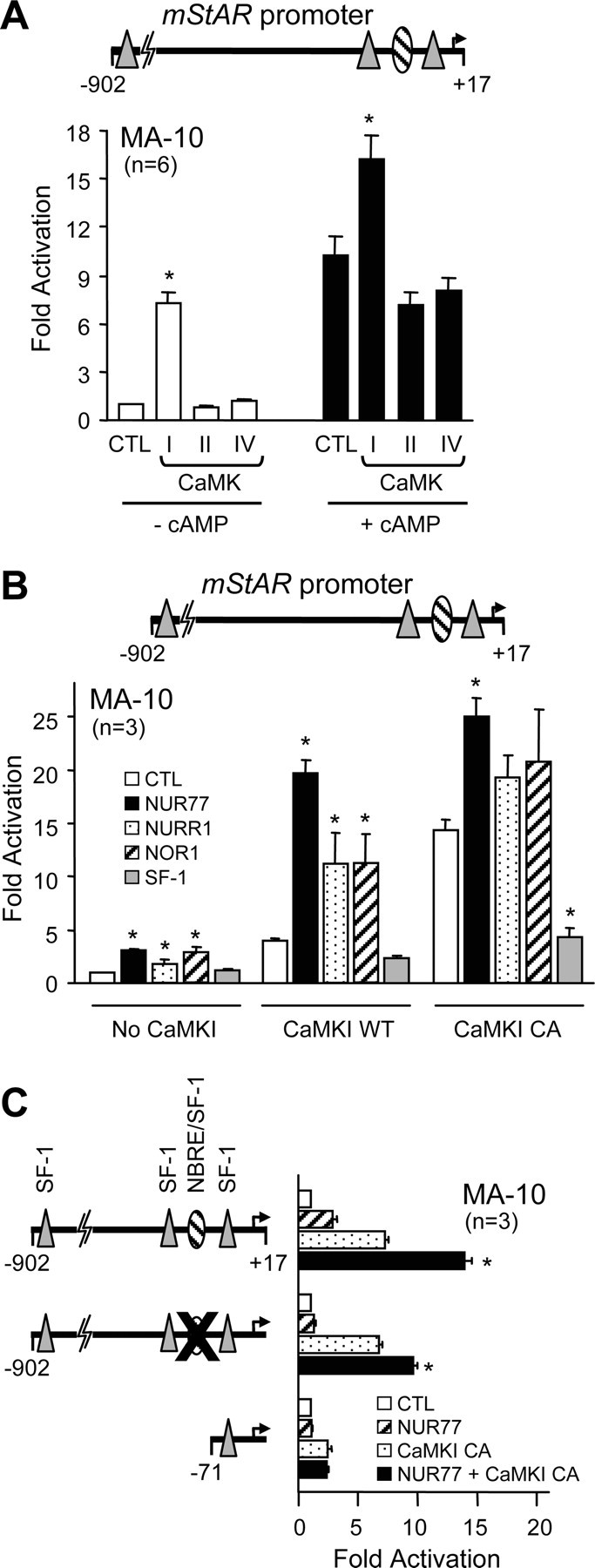
CaMKI Synergizes with NUR77 on the Mouse StAR Promoter
A, CaMKI, but not CaMKII or CaMKIV, activates the StAR promoter. MA-10 Leydig cells were cotransfected with a −902- to +17-bp mouse StAR promoter construct along with an empty expression vector (CTL) or expression vectors encoding wild-type CaMKI, CaMKII, or CaMKIV in the absence (white bars) or presence (black bars) of 0.5 mm (Bu)2-cAMP. B, NUR77 family members transcriptionally cooperate with CaMKI. MA-10 Leydig cells were cotransfected with a −902- to +17-bp mouse StAR promoter construct along with an empty expression vector (CTL) or expression vectors for NUR77 family members (NUR77, NURR1, and NOR1) and SF-1 in the absence or presence of expression vectors encoding either wild-type (WT) or a constitutively active (CA) form of CaMKI. C, The NBRE/SF-1 element at −95 bp contributes to the NUR77/CaMKI cooperation. MA-10 Leydig cells were cotransfected with an empty expression vector (white bars) or expression vectors for NUR77 (hatched bars), CaMKI CA (stippled bars), and NUR77 + CaMKI CA (black bars) along with a wild-type −902- to +17-bp StAR reporter, a reporter harboring a two-nucleotide mutation in the NBRE/SF-1 element at −95 bp (CCATCCTTGA to CCATAATTGA), or a −71- to +17-bp deletion construct. The mutated element is represented by a large X. The number of experiments, each performed in duplicate, is indicated. Results are shown as fold activation over control (±sem). *, Statistically significant difference from the respective controls (A and B); *, difference that is statistically significant from NUR77 or CaMKI alone (C).
