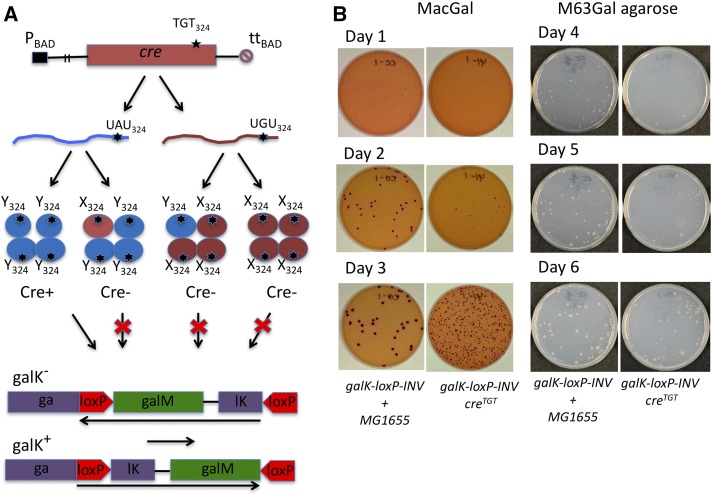
Figure 1.
The principles of the creTGT/galK-loxP-INV assay designed for detection of G→A transcription errors in E. coli. (A) Flowchart of the assay. A cre gene with a TAT to TGT mutation in codon 324 was placed into the ara operon of the E. coli chromosome to ensure low-level expression of the totally inactive Cre Y324C protein from the PBAD promoter. Infrequent G→A transcription misincorporation events restore the wild-type Tyr324 residue in Cre yielding transient Cre recombination activity. (B) Plating efficiency assay used to quantitate preexisting Gal+ as a measure of transcription misincorporation errors. The apparent frequency of Gal−→Gal+ events is quantitated as a number of red colonies on indicator MacConkey Galactose (MacGal) plates or Gal+ prototrophic colonies on selective M63Gal agarose plates. The time window for detection of preexisting Gal+ is determined using a reference culture (shown as galK-loxP-INV + MG1655), which is composed of the defined small number of Gal+ wild-type MG1655 cells (∼60–80 cells) and the Gal− galK-loxP-INV cells (104–106) containing no Cre reporter and, therefore, yielding no Gal+ colonies. In this setup, MG1655 cells produce red Gal+ colonies on an outgrowth of the Gal− galK-loxP-INV cells (the first column). Time when these colonies appear provides an important information on a time window for counting the Gal+ colonies derived from Cre-mediated recombination in galK-loxP-INV/creTGT cells (shown in the second column). A number of the Gal+ colonies significantly increased after 3-day plating of galK-loxP-INV/creTGT cells, but not the reference galK-loxP-INV + MG1655 cells, which was expected because the Cre-mediated recombination continued in galK-loxP-INV/creTGT cells after they have already been plated on MacGal. In the example representing herein the quantitation of the G→A transcription error in the wild-type background (galK-loxP-INV/creTGT cells), it takes 2 days to detect preexisting Gal+ colonies on MacGal agar plates (the middle row) and up to 6 days to detect the colonies on the M63Gal agarose plates (the bottom row).