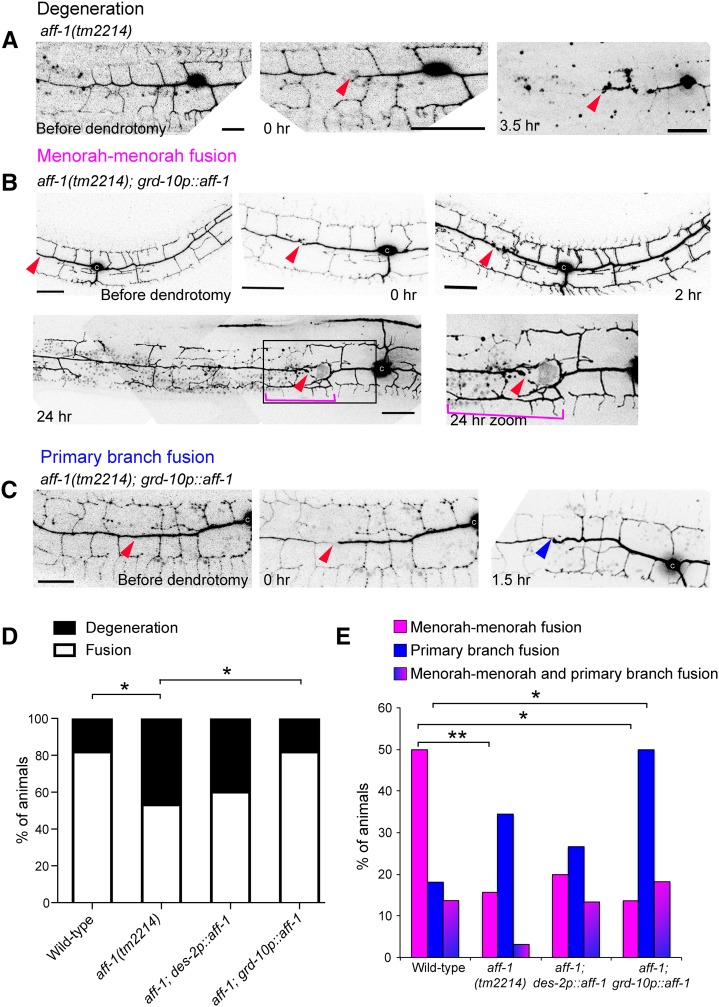
Figure 7.
aff-1 dendritic reconnection patterns are rescued cell nonautonomously. (A) Dendrite regeneration following PVD nanosurgery in aff-1(tm2214) mutant animal. PVD is shown before and after nanosurgery (t = 0 and 3.5 hr). In noninjured aff-1 mutant animals, PVD branching pattern is unaffected. After injury, fusion does not occur and the distal processes undergo degeneration (t = 3.5 hr). (B) Dendrite regeneration following PVD nanosurgery in aff-1(tm2214); grd-10p::aff-1 animals. PVD is shown before and after nanosurgery (t = 0, 2, and 24 hr). PVD reconnection occurred through fused menorahs (magenta bracket). Red arrowhead marks site of injury. Primary branches did not fuse (red arrowhead). (C) Dendrite regeneration following PVD nanosurgery in aff-1(tm2214); grd-10p::aff-1 animals. PVD is shown before and after nanosurgery (t = 0 and 1.5 hr). PVD reconnection occurred through primary fusion (blue arrowhead). (D) Quantification of the fusion vs. degeneration outcomes in wild-type, aff-1 mutant animals, and aff-1 mutant with tissue-specific aff-1 expression (des-2 for PVD and grd-10 for seam cells). Statistics were calculated using Fischer’s exact test. *P < 0.05. (E) PVD postinjury outcomes displayed in color-coded bar graphs as magenta = menorah–menorah fusion, blue = primary–primary fusion, magenta and blue = menorah–menorah fusion and primary–primary fusion, and black = degeneration. Wild-type n = 22, aff-1(tm2214) n = 32, aff-1(tm2214);des-2p::aff-1 n = 15, and aff-1(tm2214); grd-10p::aff-1 n = 22. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. Dendrotomy site = red arrowhead, fused menorah = magenta bracket, and primary fusion = blue arrowhead. Bar, 20 μm.