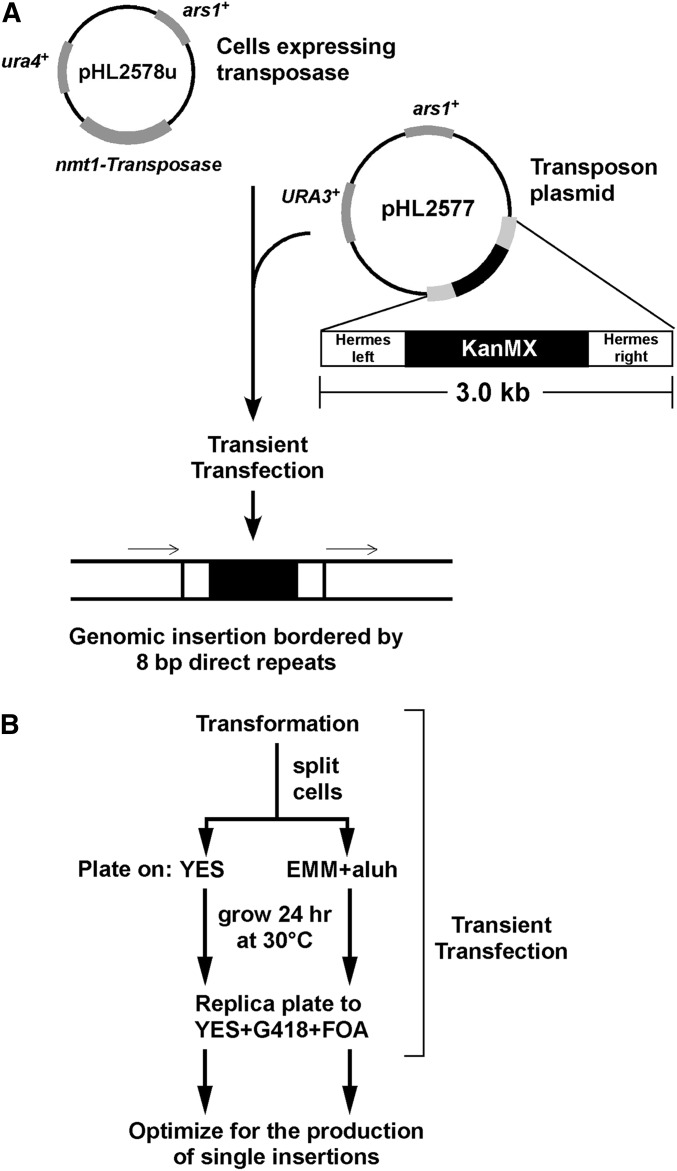
Figure 1.
A transient transfection assay to generate mutants with single-transposon insertions. (A) Cells grown under selection for the pHL2578u plasmid expressing the Hermes transposase from the nmt1 promoter under inducing conditions. The pHL2577 transposon donor plasmid contains the ends of the Hermes transposon flanking a kanamycin selectable marker (KanMX) that confers resistance to G418. Introducing the transposon plasmid into cells expressing the transposase allows insertion of the transposon into the genome, generating a target site duplication of 8 bp (indicated by thin arrows). (B) Cells expressing transposase were transformed with different amounts of the transposon plasmid. To monitor whether continuous expression of transposase impacted transposition, half of the transformed cells were plated onto either noninducing (YES) or inducing (EMM) nonselective media. The EMM plates contained supplements to complement cellular auxotrophies (Moreno et al. 1991). After 24 hr of growth to allow plasmid loss, the lawn of cells was replica plated onto medium that selects for the transposon (G418-resistance) and against the ura4+ and URA3+ genes (FOA) on the two plasmids. The yield of colonies bearing transposon insertions is shown in Table 1. aluh, adenine, leucine, uracil, and histidine; FOA, 5’-fluoroorotic acid; YES, yeast extract sucrose.