Figure 8.
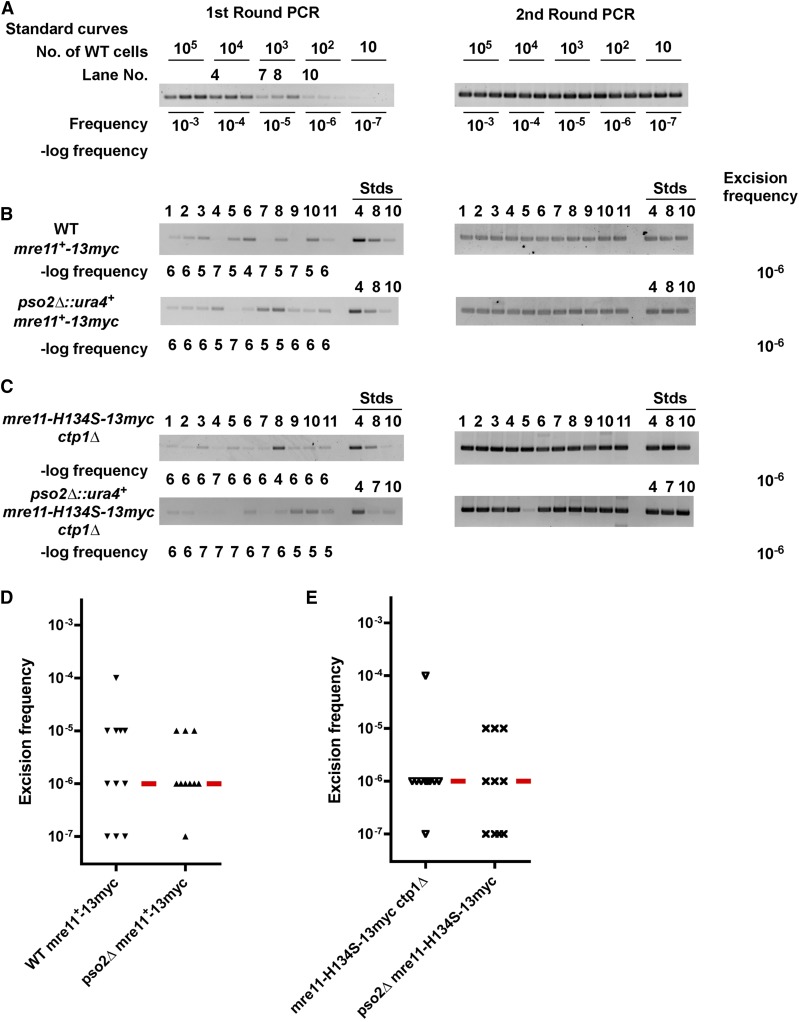
The S. pombe homolog of in vitro hairpin nuclease Pso2 is not required for excision. S. cerevisiae Pso2 can cleave DNA hairpins in vitro (Tiefenbach and Junop 2012), suggesting that the S. pombe homolog may account for the excision healing activity in mre11 mutants that lack nuclease activity. Hermes excision was analyzed with a modified assay (see Materials and Methods) that analyzed 11 colonies. (A) A standard curve constructed using a culture of 2 × 107 cells that also contained the indicated number of wild-type cells to model the excision event as in Figure 2. The lane numbers indicate genomic DNA samples that were amplified in parallel with the colonies in (B) and (C). (B) Hermes excision frequencies in the epitope-tagged mre11-13myc strains are not affected by loss of Pso2 (P = 0.84 by Mann–Whitney test). “Stds” refers to samples from the standard curve in (A) that were amplified at the same time as each of the colonies shown. The numbers above the Stds lanes refer to the lane numbers shown in (A). (C) Excision frequencies in the epitope-tagged mre11-H134S-13myc ctp1∆ double mutant strains are not affected by loss of Pso2 (P = 0.69 by Mann–Whitney test). (D) Graphical representation of the excision frequencies in (B), where the red bar denotes the median excision frequency. (E) Graphical representation of the excision frequencies in (C). Lane No., lane number; wild-type, WT.