Fig. 5.
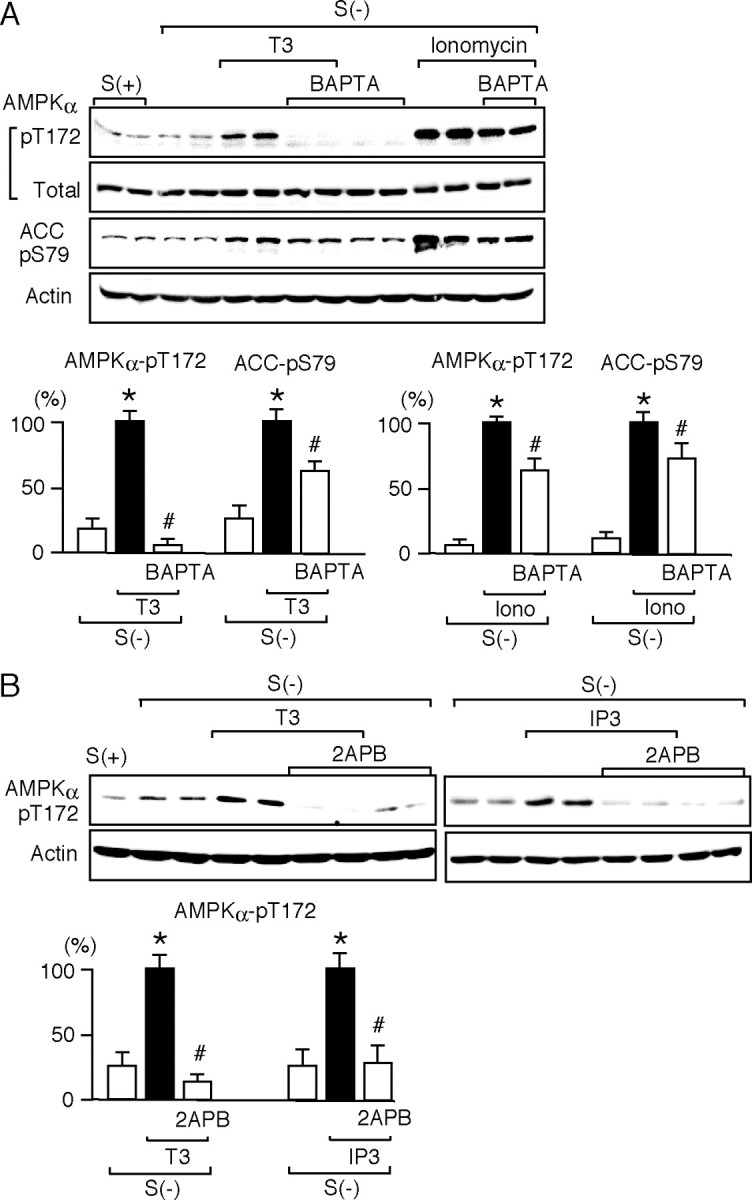
T3-Dependent Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization Is Associated with the Phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC
A, HeLa cells were cultured with [S(+)] or without [S(−)] serum for 12 h. They were pretreated for 15 min with 10 μm BAPTA and treated for 30 min with 10 nm T3 or 1 μm ionomycin (Iono) in the presence of BAPTA. Whole-cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against phospho-AMPK α-subunit (pT172), AMPK α-subunit (total), phospho-ACC (pS79), and actin. The experiments were performed in duplicate cultures. Similar results were obtained from separate experiments. In densitometric analysis, the phospho-AMPK and phospho-ACC levels were normalized to the actin levels and expressed as percentages of the levels in cells treated with T3 or ionomycin alone. Results are means ± sd (n = 4). *, P < 0.05 vs. the levels in S(−) cells; #, P < 0.05 vs. the levels in cells treated with T3 or ionomycin alone. B, HeLa cells were cultured with [S(+)] or without [S(−)] serum for 12 h. They were pretreated for 15 min with 100 μm 2APB and treated with 10 nm T3 for 30 min or 1 μm IP3 for 5 min in the presence of 2APB. Whole-cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against phospho-AMPK α-subunit (pT172) and actin. The experiments were performed in duplicate cultures. Similar results were obtained from separate experiments. In densitometric analysis, the phospho-AMPK levels were normalized to the actin levels and expressed as percentages of the levels in cells treated with T3 or IP3 alone. Results are means ± sd (n = 4). *, P < 0.05 vs. the levels of S(−); #, P < 0.05 vs. the levels of T3 alone or the levels of IP3 alone.
