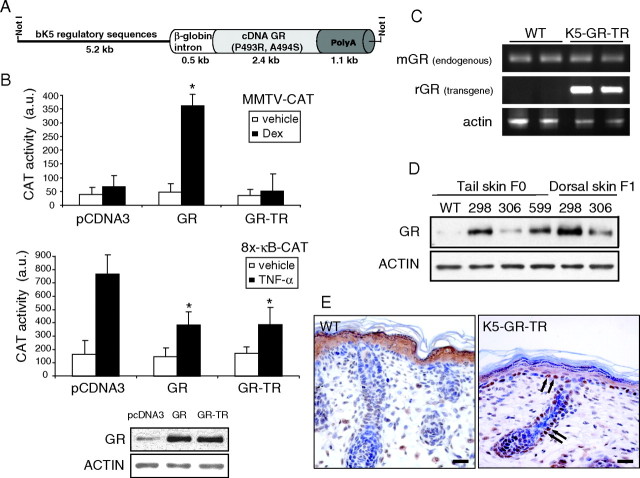
Fig. 1.
Generation of K5-GR-TR Transgenic Mice Expressing a Mutant GR in Keratinocytes that Is Defective in Transactivation but Effective in Transrepression
A, Scheme of the construct K5-GR-TR. The cDNA of GR containing a double mutation (P493R, A494S) was placed under control of bovine K5 (bk5) regulatory sequences. B, PB keratinocytes were transiently transfected with either MMTV-CAT or 8x-κB-CAT reporter plasmids along with expression vectors encoding for empty vector (pcDNA3), K5-GR, or K5-GR-TR. After depletion of endogenous GCs, cells were treated with either vehicle or 1 μm Dex for 6 h to determine MMTV-CAT activity. In transfections using 8x-κB-CAT reporter, vehicle or TNF-α (10 ng/ml) were added for 4 h before measuring CAT activity (a.u, arbitrary units). Data presented are average of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate sd. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences relative to pCDNA3-transfected cells, as analyzed by Student’s t test (*, P < 0.0005). Expression levels for the WT and mutant GR upon transfection were checked by immunoblotting (lower panel). C, RT-PCR analysis showing the endogenous [mouse GR (mGR)] and transgene [rat GR (rGR)] transcript levels in the skin of WT and K5-GR-TR adult littermates. D, Immunoblotting using whole-cell extracts from tail and dorsal skin of three transgenic founders (298, 306, and 599) to check the relative expression levels of GR. E, Immunolocalization of GR in dorsal skin paraffin sections from newborn WT and transgenic mice. Arrows indicate the nuclear localization of GR in the interfollicular basal epithelium and the outer root sheath of HFs in transgenic skin. Scale bar, 25 μm.