Fig. 4.
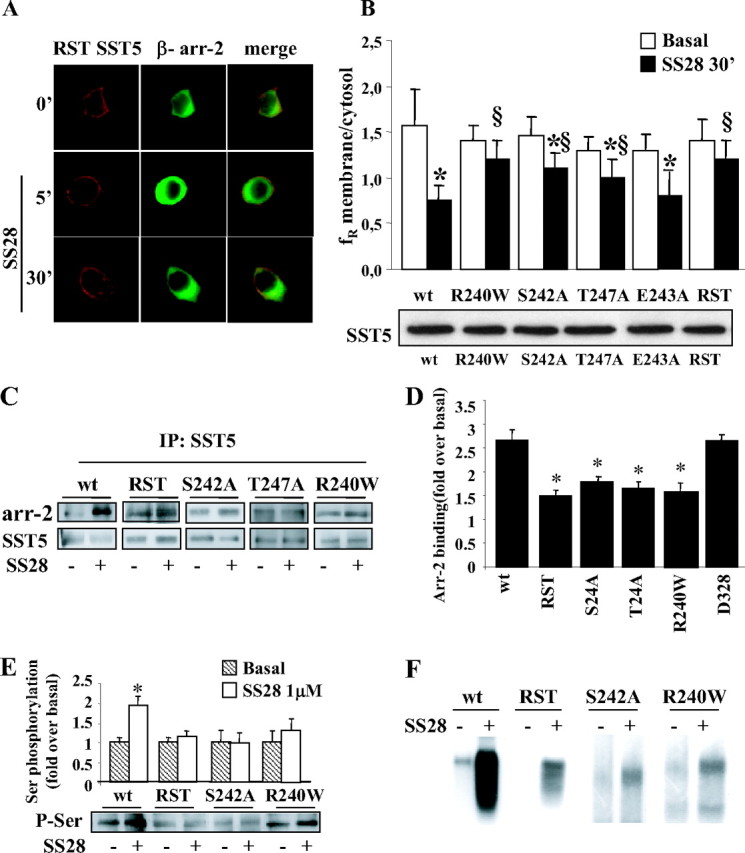
Effects of Introducing Mutations within the Third Cytoplasmic Loop of SST5 (Red) on β-Arrestin-2 (Green) Translocation and Receptor Internalization
A, GH3 cells transiently cotransfected with β-arrestin-2 and SST5 with simultaneous mutations of R240, S242, and T247 (RST) were incubated with SS28 1 μm for 5 and 30 min. We created three-point mutant receptors by site-directed mutagenesis in which these three residues were replaced by Ala (S242A, E243A, and T247A mutants). We also tested a naturally occurring SST5 third-loop mutant (R240W) previously found in one acromegalic patient resistant to SS analogs. As shown here for RST mutant as a representative example, mutant receptors were correctly targeted to the plasma membrane. No β-arrestin translocation was observed after 5 min SS28 incubation and, accordingly, RST mutant internalization was almost completely abolished. Fixed cells were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. The figure shows representative images from one of at least five individual experiments. B, SST5 third-loop mutants (R240W, S242A, T247A, E243A, and RST) internalization was evaluated using ImagePro-Plus 6.0 software. Mean membrane to intracellular fluorescence ratio (fR) was calculated. For each group, at least 30 cells from three independent transfections were analyzed and the mean value was used for the graph. *, P < 0.01 vs. basal; §, P < 0.01 vs. wild-type SST5 + SS28 30′. The lower panel shows a representative Western blot of wild-type and third-loop mutated SST5 receptors immunoprecipitated from cell membrane extract in basal conditions. C, Association of third-loop mutants SST5 with β-arrestin-2. GH3 cells transiently cotransfected with wild-type, RST, S242A, T247A, or R240W SST5 and β-arrestin-2 were washed and incubated at 37 C with 1 μm SS28 for 5 min before cross-linking. Lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with SST5 antibody, and the presence of β-arrestin-2 and SST5 was detected using anti-GFP and anti-SST5 antibody, respectively. The figure shows a representative experiment. D, The figure compares the association of β-arrestin-2 to wild-type, third loop-mutated, and D328-deleted SST5 receptors. The analysis of the data obtained from five separate experiments was performed with the image analysis program NIH ImageJ. β-Arrestin-2 binding is expressed as the fold increase relative to unstimulated cells and represents mean ± se. *, P < 0.05 vs. wild type. E, Analysis of wild-type and mutated SST5 phosphorylation. GH3 cells transiently transfected with wild type or mutated SST5 were incubated with SS28 1 μm for 5 min. SST5 was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates, and Western blot analysis was performed using antiphosphoserine antibody (lower panel). Loading of equal amounts of receptor proteins in each lane was confirmed with anti-SST5 antibody. The upper panel shows the analysis of the data obtained from five separate experiments performed with the image analysis program NIH ImageJ and represents mean ± se. *, P < 0.05 vs. basal. The level of agonist-induced serine phosphorylation, expressed as the fold increase relative to unstimulated cells, was reduced for RST (1.15-fold over basal), S242A (0.93-fold over basal), and R240W (1.38-fold over basal) receptor with respect to wild-type SST5 (1.93-fold over basal). F, Autoradiogram of SDS-PAGE analysis of immunoprecipitates from whole-cell phosphorylation assays. GH3 cells were transiently transfected with the appropriate plasmids for 48 h, labeled with [32P]orthophosphate, and incubated with 1 μm SS28 for 5 min. SST5 was immunoprecipitated, and the samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. A representative experiment is shown. arr-2, arrestin-2; wt, wild type; P-Ser, phosphoserine.
