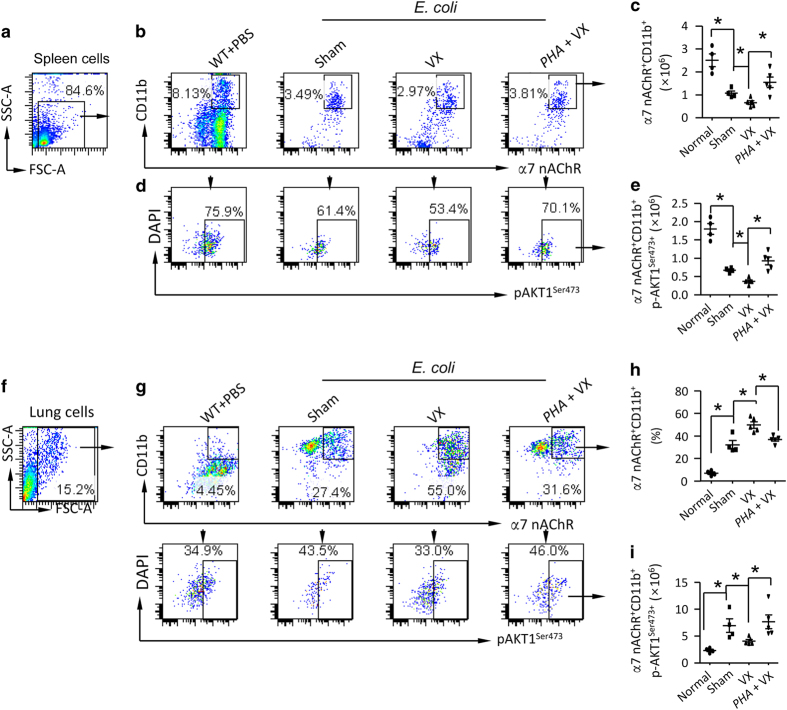
Figure 4.
Vagal-α7 nAChR signaling engages with phosphorylation of AKT1Ser473+ to prevent egress of α7 nAChR+CD11b+ cells from spleen and recruitment of these cells towards E. coli-injured lungs. (a–e) Vagal-α7 nAChR signaling regulates of p-AKT1Ser473+in splenic α7 nAChR+CD11b+cells during E. coli pneumonia. Sham, vagotomized and vagotomized plus PHA568487 (0.4 mg kg−1 pretreated 15 min prior to E. coli (2.5×106 cfu) and given every 6 h, IP). The mice were killed 24 h after infection. The spleen cells were collected and labeled with the indicated fluorescent antibodies. The granular cells were gated (a). The α7 nAChR+CD11b+ cells were first analyzed and then calculated the percentage of p-AKT1Ser473+ cells (b–e). N=4–5 in each group. *P<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (f–i) Flow cytometry analysis of α7 nAChR+CD11b+ cell population the lung during E. coli pneumonia. Using the same experimental setting as (a–e), the lung cells were collected and labeled with the indicated fluorescent antibodies. The granular cells were gated (f). The α7 nAChR+CD11b+ cells and α7 nAChR+CD11b+p-AKT1Ser473+ cells were analyzed (g). The percentage of α7 nAChR+CD11b+ cells and number of α7 nAChR+CD11b+p-AKT1Ser473+ cells were calculated (h, i). N=4–5 in each group. *P<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. Data are presented as mean±s.d.