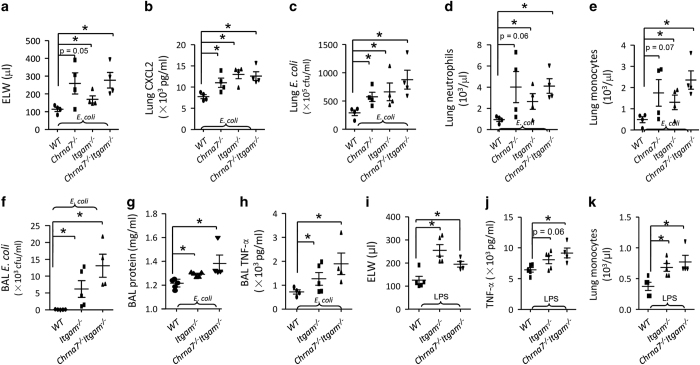
Figure 9.
Deletion of Itgam or/and Chrna7 worsens E. coli and LPS-induced ALI. Double deletion of Chrna7 and Itgam aggravates E. coli-induced ALI (a–e). The wildtype, Chrna7−/−, Itgam−/− and Chrna7−/−Itgram−/− mice were, respectively, challenged with E. coli (2.5×106 cfu) intratracheally. The mice were killed at 24 h after E. coli challenge. ELW (a), CXCL2 levels (b) in the supernatant of lung homogenate, lung E. coli colonies (c), lung neutrophils (d) and lung monocytes (e) were measured. N=4 in each group, *P<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. Data are presented as mean±s.d. Double deletion of Chrna7 and Itgam increases BAL inflammatory parameters in E. coli-induced ALI (f–h). The wildtype, Itgam−/− and Chrna7−/−Itgram−/− mice were, respectively, challenged with E. coli (2.5×106 cfu) intratracheally. The mice were killed at 24 h after E. coli challenge. BAL was collected to measure BAL E. coli colonies (f), BAL protein (g) and BAL TNF-α (h). N=4 in each group, *P<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. Data are presented as mean±s.d. (i–k) Double deletion of Chrna7 and Itgam exacerbates LPS-induced ALI. The wildtype, Itgam−/− and Chrna7−/−Itgam−/− mice were, respectively, challenged with LPS (5 mg kg−1) intratracheally. The mice were killed at 24 h after LPS challenge. ELW (i), TNF-α level (j) in the supernatant of lung homogenate and lung monocytes (k) were analyzed. N=5 in each group, *P<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. Data are presented as mean±s.d.