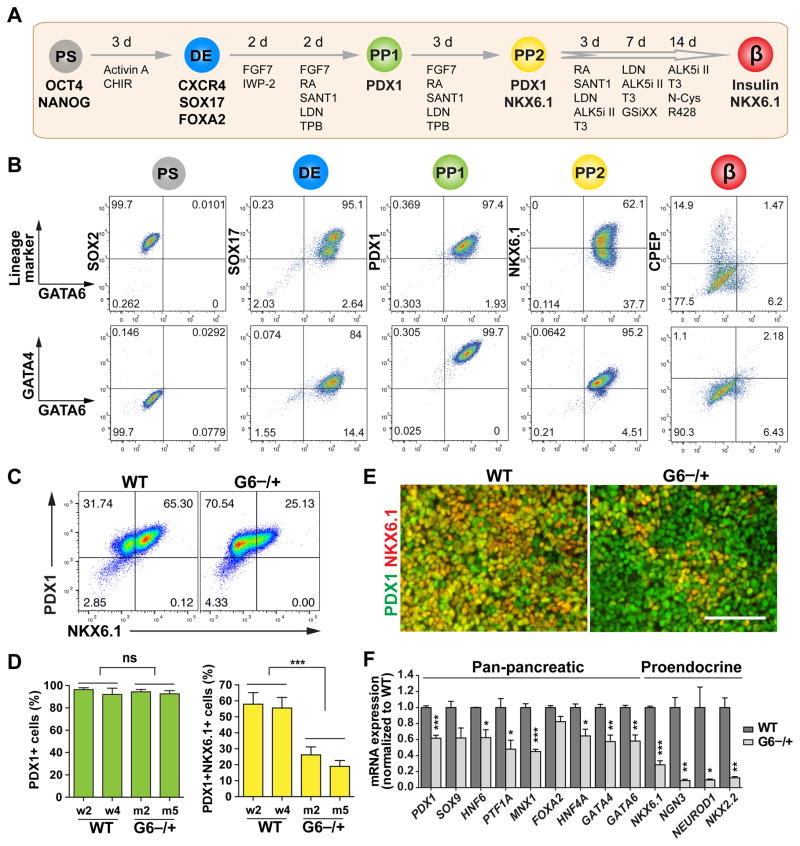
Figure 4. GATA6 haploinsufficiency in the specification of PDX1+NKX6.1+ pancreatic progenitor cells.
(A) Schematic of modified 2nd-generation differentiation protocol toward β-like stage from hPSCs. The key lineage markers at each stage are shown. Chemicals and durations for each differentiation stage are indicated. hPS: undifferentiated hPSC stage; DE: definitive endoderm stage; PP1: early pancreatic progenitor stage; PP2: pancreatic endoderm progenitor stage; β: β-like stage. From PP2 to β-like stage, the cells were cultured at air-liquid interface. See also Table S3 for detailed differentiation medium recipes.
(B) Representative FACS dot plots of GATA6 co-staining with stage-specific lineage markers or GATA4 for each stage.
(C) Representative FACS dot plots for PDX1 and NKX6.1 co-staining at the PP2 stage.
(D) Quantification of PDX1+ cells and PDX1+NKX6.1+ cells at the PP2 stage based on FACS analysis from 3 independent experiments. The statistics was done by comparing the mutant group with the WT group. The hPSC lines with the same genotypes were treated as one group (n=6).
(E) Representative images for PDX1 and NKX6.1 expression at the PP2 stage.
(F) RT-qPCR analysis of pancreatic progenitor marker expression at the PP2 stage (n=4). Genes labeled in red were not expressed in the PP1 cells. t-test with two-tailed distribution and two-sample equal variance was used to determine the significance in this figure panels D and F to compare with WT group.
All data in this figure were generated from H1 lines using the 2nd-generation differentiation protocol (Table S3). See also Figures S2 and S3.