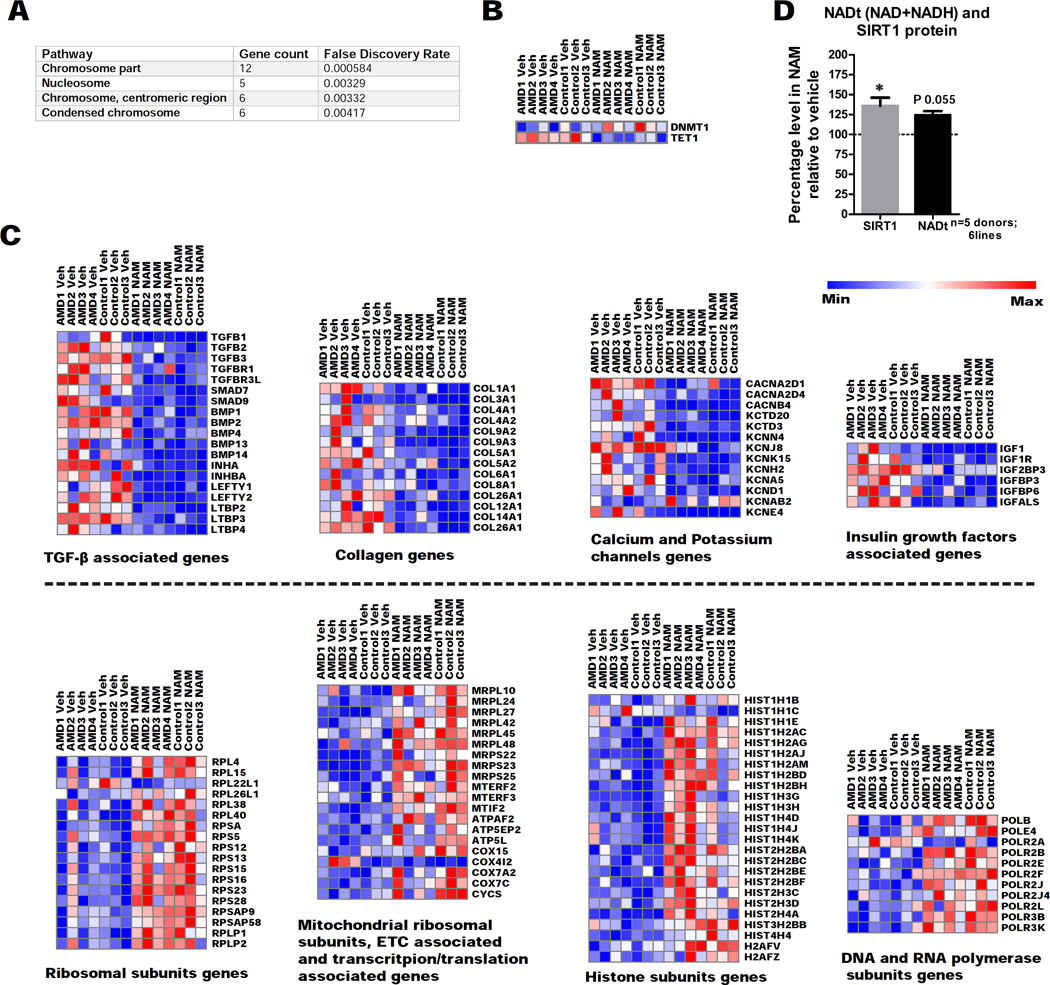
Figure 6. NAM acts on aging associated pathways and increases expression of SIRT1 protein and NAD biosynthetic pathway in hiPSC-RPE.
(A) GO functional enrichment for cellular components of exclusively upregulated genes in NAM treated hiPSC-RPE compared to vehicle from RNA-seq analysis, using the STRING database (n=7 donors; 4 AMD and 3 control; 7 lines).
(B) Altered expression of DNA methylation associated genes detected by RNA-seq analysis of NAM treatment (veh: vehicle) (n=7 donors; 4 AMD and 3 control; 7 lines).
(C) Altered expression of functionally related genes detected by RNA-seq analysis of NAM treatment (veh: vehicle) (n=7 donors; 4 AMD and 3 control; 7 lines).
(D) SIRT1 protein and total NAD (NAD+NADH) levels measured 40–48 hours and 12–18 hours, respectively after the last medium change from 10mM NAM treated hiPSC-RPE relative to vehicle (baseline defined as 100%). Data are expressed as mean± SEM (n=5 donors; 2 AMD and 3 Control; 6 lines). Paired Student’s t-test (two-tailed) was used for statistical analysis (*= p<0.05).